A Relay Electrical Diagram is a vital tool used in electrical engineering to represent how relays function within an electrical system. Relays are electromechanical switches that allow a small control signal to operate a larger power circuit. They play a crucial role in automation, protection systems, and circuit control by isolating different parts of a system. Understanding the relay electrical diagram helps engineers and technicians design, troubleshoot, and maintain complex electrical circuits with ease. This article will provide a detailed explanation of the components, functions, and significance of a relay electrical diagram.
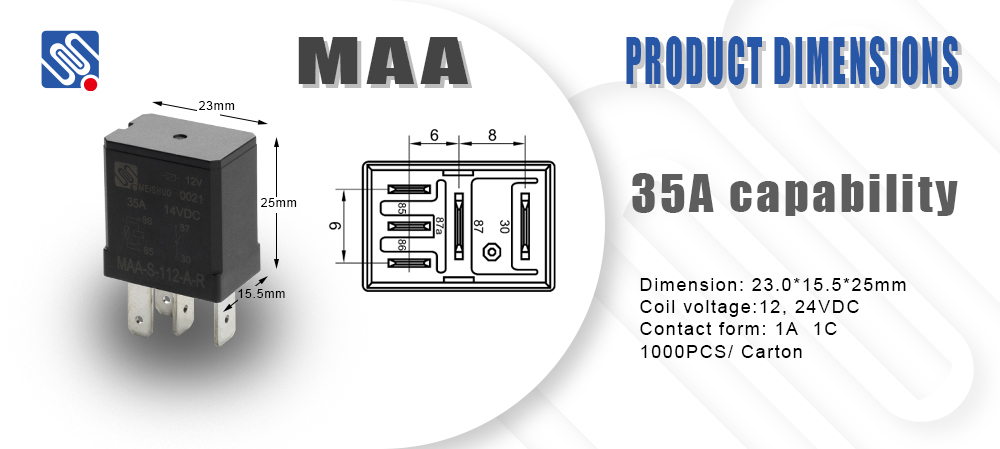
What is a Relay? A relay is an electrical device that opens or closes a set of contacts to control the flow of electricity. It uses a small input voltage (control signal) to activate a coil inside the relay. When current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field, which moves an armature that either opens or closes the relay’s contacts. The contacts can either be normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC), depending on the design of the relay. Relays are widely used in automation systems, protective circuits, and applications where isolation between the control and power circuits is required. Examples include motor control systems, circuit breakers, alarm systems, and telecommunications.