Relays have long played a crucial role in electrical engineering, serving as the brains behind countless systems by providing efficient control over high-power devices. One notable component in this domain is the 24V 30A relay, which is widely used across various applications due to its reliability, versatility, and capacity to handle significant loads. This article delves into the features, operation, and practical uses of the 24V 30A relay.
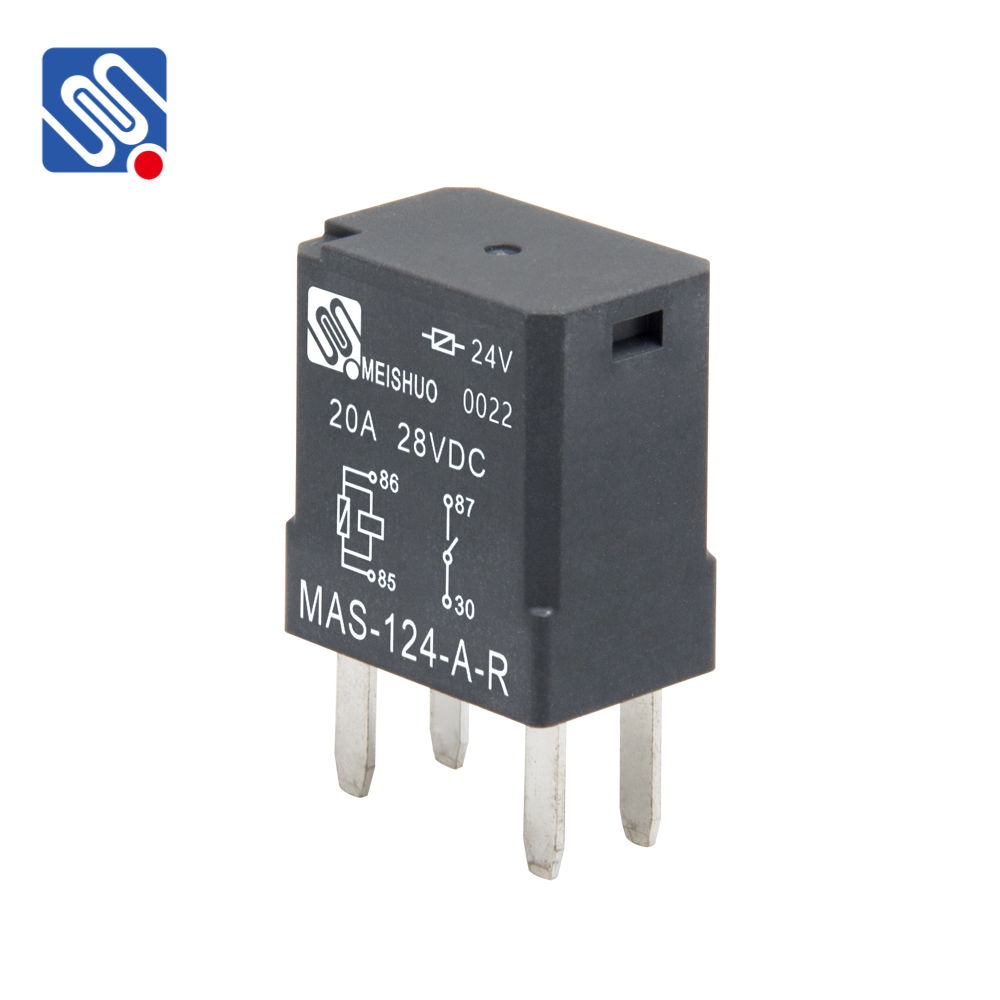
Understanding the 24V 30A Relay At its core, a relay is an electromechanical switch that allows one circuit to control another circuit, enabling low-power devices to control high-power loads. The 24V 30A relay, as its name suggests, operates at a voltage level of 24 volts and can handle a current of up to 30 amperes. This makes it suitable for applications that involve substantial power requirements. The relay typically consists of several components, including an electromagnet, an armature, and contacts. When a voltage is applied to the relay’s coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the armature, causing it to move and either connect or disconnect the contacts. This action opens or closes the associated circuit, thus controlling the flow of electricity to connected devices.