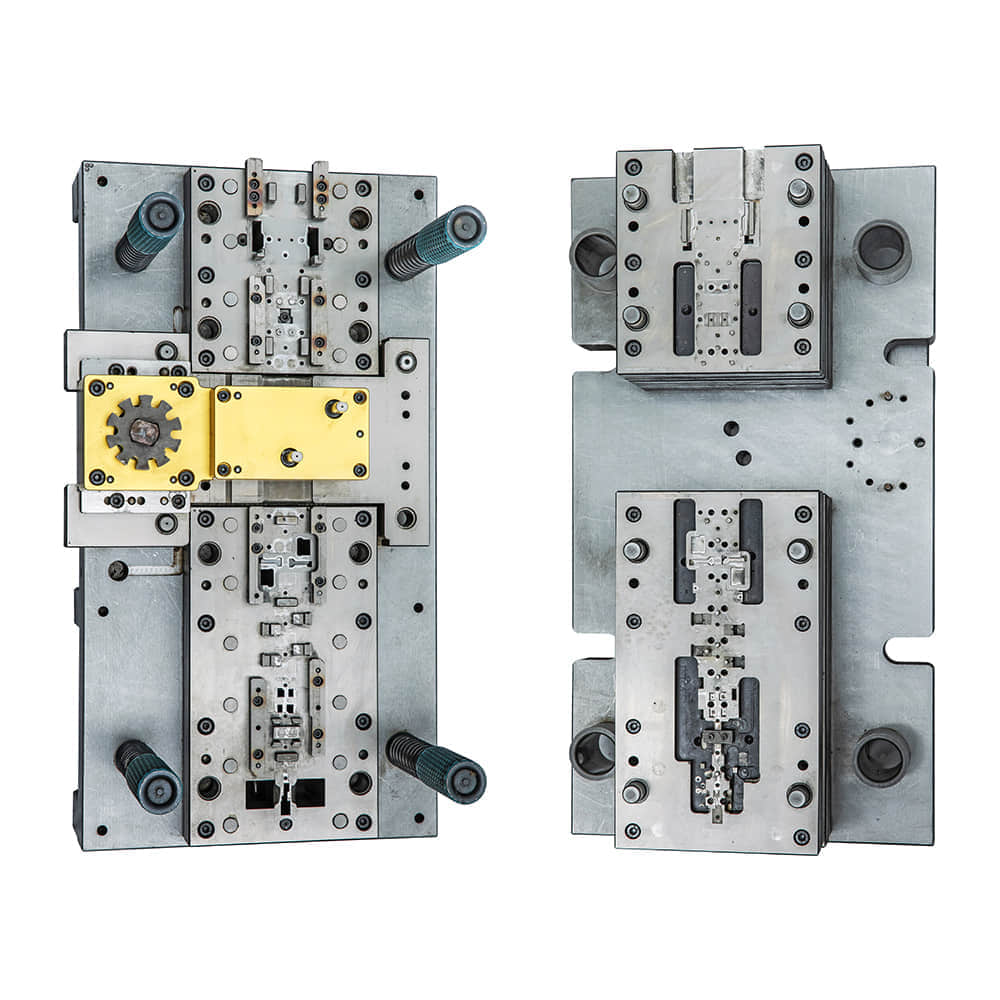
In the world of manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. One essential tool that embodies these qualities is the metal stamping die. Metal stamping dies are the unsung heroes behind many of the everyday items we take for granted, from the lids on our beverage cans to the intricate components in our electronic devices. In this article, we will delve into the world of metal stamping dies, exploring their significance, design intricacies, and the vital role they play in modern manufacturing.
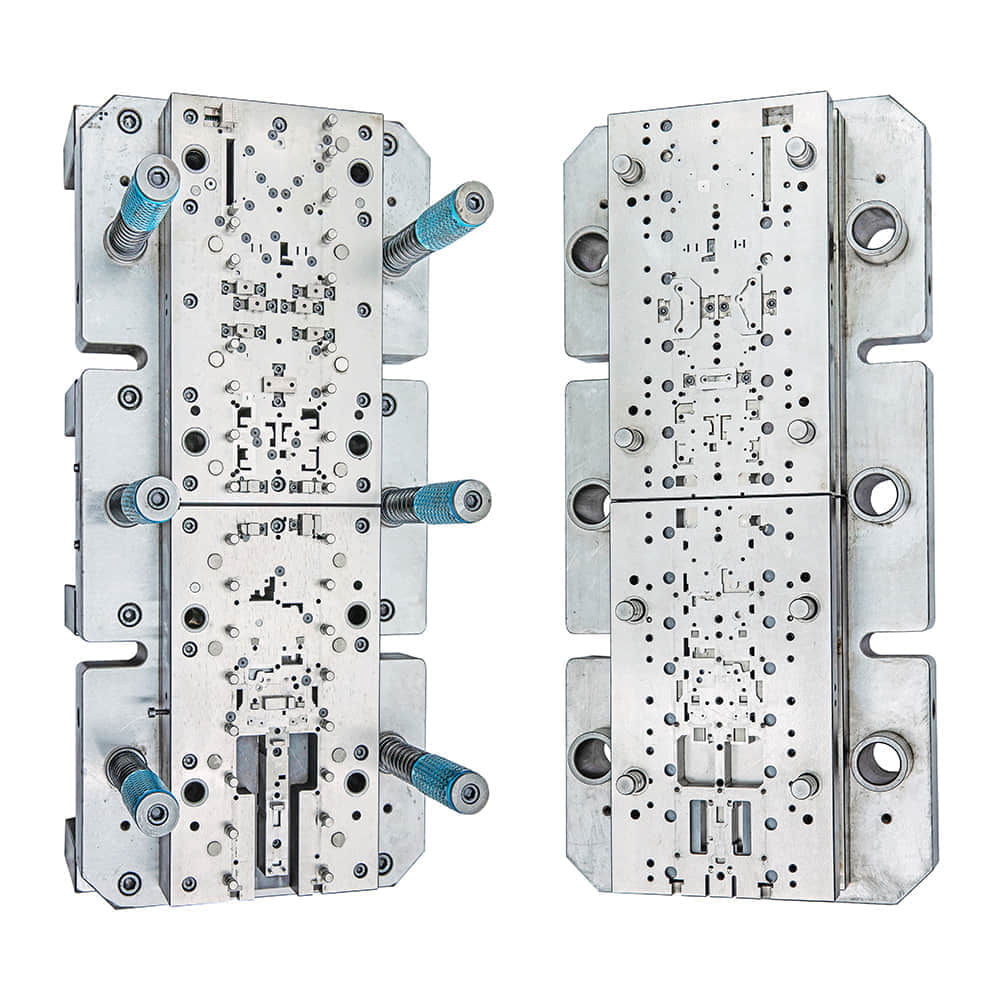
The Significance of Metal Stamping Dies
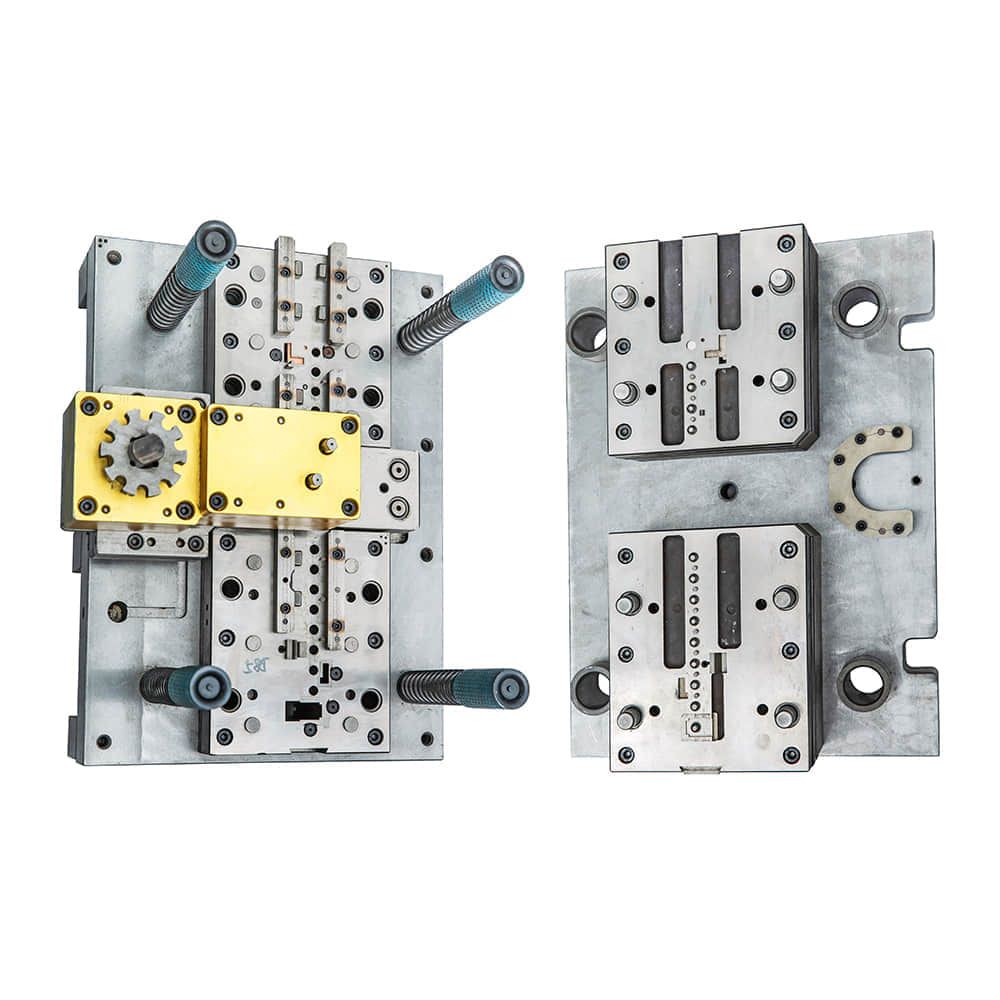
Metal stamping dies, often simply referred to as dies, are specialized tools used in the metalworking industry to shape, cut, or form metal sheets into precise, repeatable shapes. They are instrumental in mass-producing components used in various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods. The significance of metal stamping dies lies in their ability to produce high-quality, identical parts at an impressive speed. These dies can endure thousands, and sometimes even millions, of cycles, maintaining consistent accuracy throughout their lifespan. This reliability and repeatability are essential for industries that demand consistency and precision, such as automotive manufacturing. Design and Manufacturing The creation of a metal stamping die is a meticulous process that requires a combination of engineering expertise and craftsmanship. Here are the key steps involved in designing and manufacturing a metal stamping die: Design Concept: The process begins with a clear understanding of the desired part’s specifications and dimensions. Engineers create a design concept that includes detailed drawings, tolerances, and material specifications. Material Selection: Choosing the right material for the die is critical. Tool steels like D2 and A2 are commonly used due to their excellent wear resistance and toughness. CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are employed to precisely shape the die’s components according to the design specifications. This process demands exceptional precision, as even the slightest deviation can affect the quality of stamped parts. Heat Treatment: After machining, the die undergoes heat treatment processes to enhance its hardness and durability. This ensures it can withstand the rigors of stamping without deformation. Assembly and Testing: Skilled toolmakers assemble the die, ensuring that all components fit perfectly. Rigorous testing follows to verify that the die functions as intended. Fine-Tuning: Even the most meticulously crafted dies may require fine-tuning to achieve the desired level of precision. This process involves trial stamping runs and adjustments as necessary. Production: Once the die is perfected, it is ready for mass production. Stamping presses, ranging from small, single-operation machines to large automated systems, are used to produce the final parts. Types of Metal Stamping Dies Metal stamping dies come in various forms to accommodate different manufacturing needs: Progressive Dies: These dies perform multiple operations in a single stroke, making them ideal for high-volume production of intricate parts. Compound Dies: Compound dies are used for parts with more complex shapes and features. They consist of multiple stations that perform different operations sequentially. Blanking Dies: Blank dies are designed to cut out flat pieces of metal from a larger sheet. They are commonly used for producing flat, simple components. Forming Dies: Forming dies are used to shape metal into three-dimensional forms, such as automobile body panels or kitchen utensils. The Impact on Manufacturing The use of metal stamping dies has revolutionized manufacturing across industries. Their ability to produce high-quality parts quickly and efficiently has lowered production costs and reduced waste. Moreover, the precision achieved with metal stamping dies ensures that parts fit and function as intended, contributing to the overall quality and safety of the end products. Innovations in die design, materials, and manufacturing techniques continue to enhance the capabilities of metal stamping dies. The ability to create increasingly intricate parts with tighter tolerances has opened up new possibilities in product design and functionality. In conclusion, metal stamping dies are the unsung heroes of modern manufacturing, enabling the efficient production of countless products we use in our daily lives. Their precision, durability, and versatility make them indispensable tools in industries that demand consistent quality and high output. As technology advances, we can expect metal stamping dies to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing.