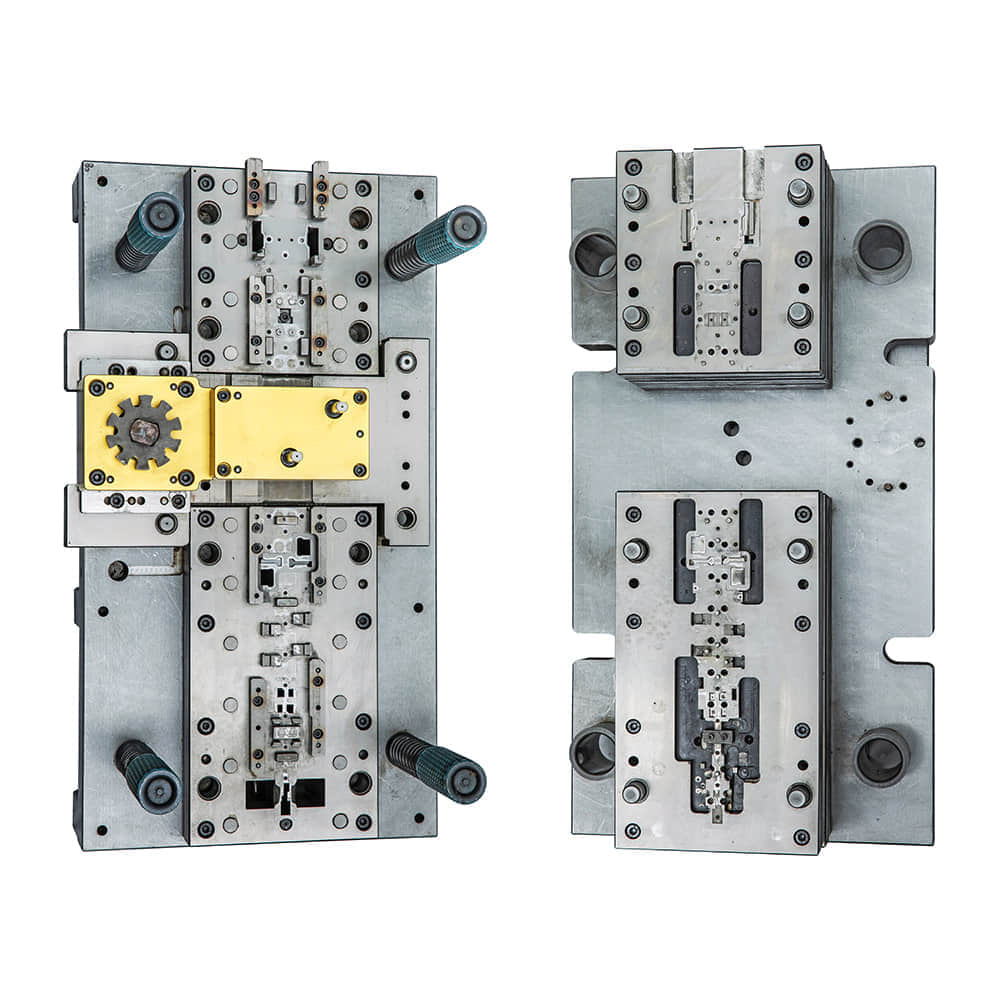
Introduction
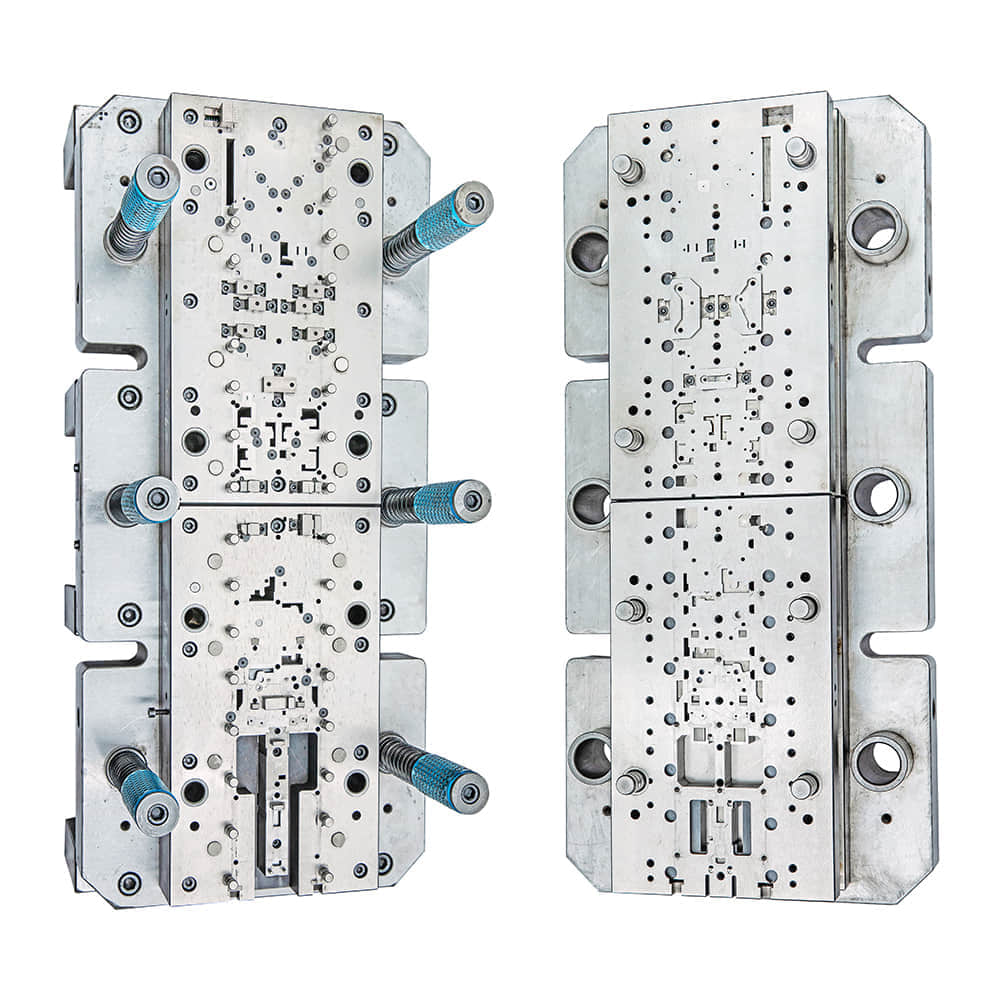
In the world of manufacturing and metalworking, precision and efficiency are paramount. One indispensable tool that plays a significant role in achieving these goals is the blanking die. With its ability to cut and shape raw materials with exceptional accuracy, the blanking die has revolutionized various industries. This article delves into the intricacies and applications of blanking dies, highlighting their importance in modern manufacturing processes.
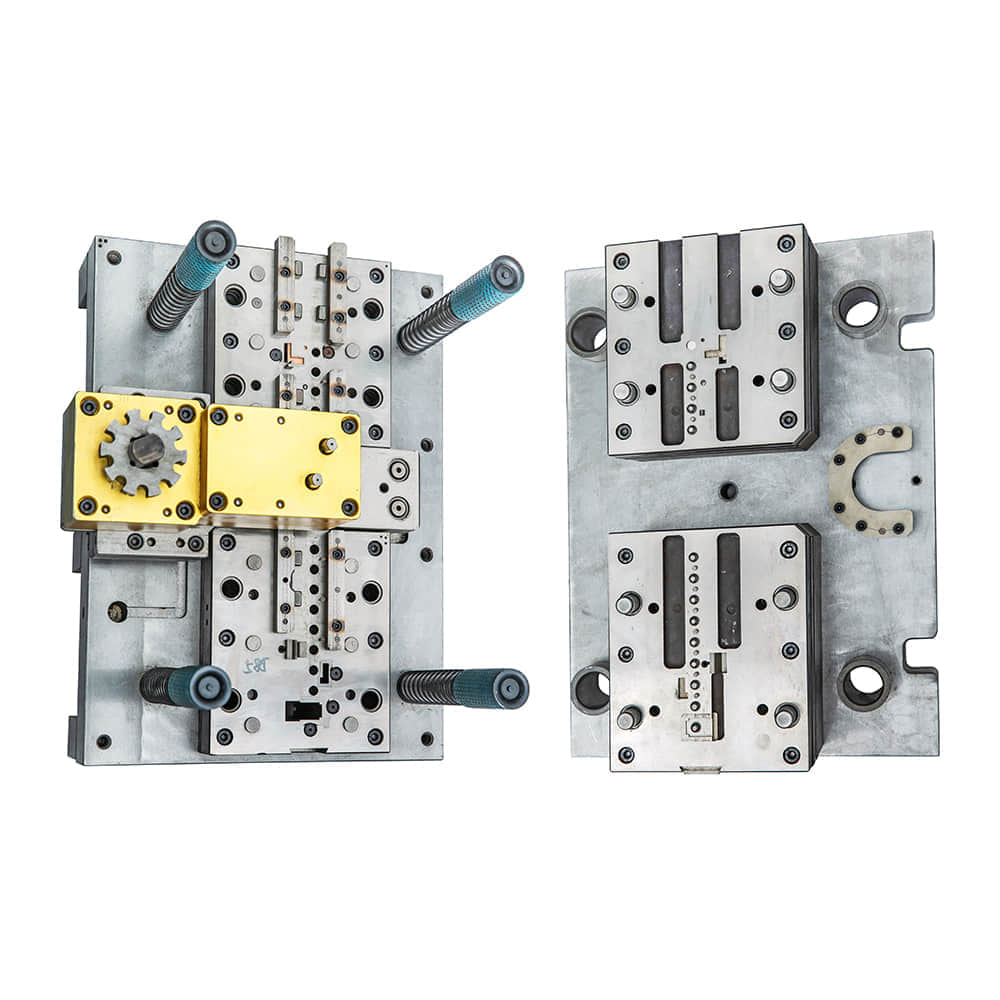
Understanding Blanking Dies A blanking die is a specialized tool used in metalworking to cut intricate shapes from sheet metal or other flat stock materials. It consists of a punch and a die, which work in tandem to shear out the desired shape. The punch exerts force on the sheet metal, while the die provides the corresponding shape’s cavity, effectively separating the desired piece from the rest of the material. This process, known as blanking, produces components with precise dimensions and clean edges. Intricacies of Design and Manufacturing Designing a blanking die requires a deep understanding of material properties, sheet thickness, and the desired finished product. Engineers meticulously create the die to accommodate the required tolerances and to minimize material wastage. The cutting edges of both the punch and the die must be properly engineered to avoid deformations and ensure a smooth cutting process. Additionally, factors such as clearance between the punch and die, material hardness, and lubrication play crucial roles in achieving optimal results. Applications in Manufacturing Blanking dies find applications in a wide range of industries, from automotive to electronics. In the automotive sector, blanking dies are used to create precise components for engines, chassis, and body panels. In electronics, they help produce intricate parts for devices such as smartphones, laptops, and appliances. Moreover, the packaging industry relies on blanking dies to manufacture metal containers with consistent shapes and sizes. The versatility of blanking dies makes them an indispensable tool for mass production of uniform components. Advantages of Blanking Dies Precision: Blanking dies offer unparalleled precision, ensuring that the cut components meet exact specifications, which is critical for industries requiring standardized parts. Efficiency: The high-speed nature of blanking processes allows for rapid production, contributing to efficient manufacturing and reduced production times. Material Utilization: By minimizing material wastage through precise cutting, blanking dies help maximize the utilization of raw materials, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Consistency: The uniformity achieved through blanking dies ensures consistent quality across the produced components, reducing defects and rejections. Challenges and Future Developments Despite their many advantages, blanking dies also face challenges. Complex shapes, thick materials, and intricate patterns can pose difficulties in achieving clean cuts without deformations. Addressing these challenges requires continuous research and development in die design, materials science, and manufacturing techniques. In the future, advancements in technology, such as the integration of automation, AI, and improved tool materials, will likely further enhance blanking die capabilities. These developments could lead to even higher precision, faster production rates, and expanded possibilities for cutting various materials, including composites and advanced alloys. Conclusion Blanking dies represent a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the creation of intricate components with unparalleled precision and efficiency. Their versatility spans multiple industries, contributing to the production of items we encounter daily. As technology continues to advance, so too will the capabilities of blanking dies, ushering in a new era of manufacturing excellence.