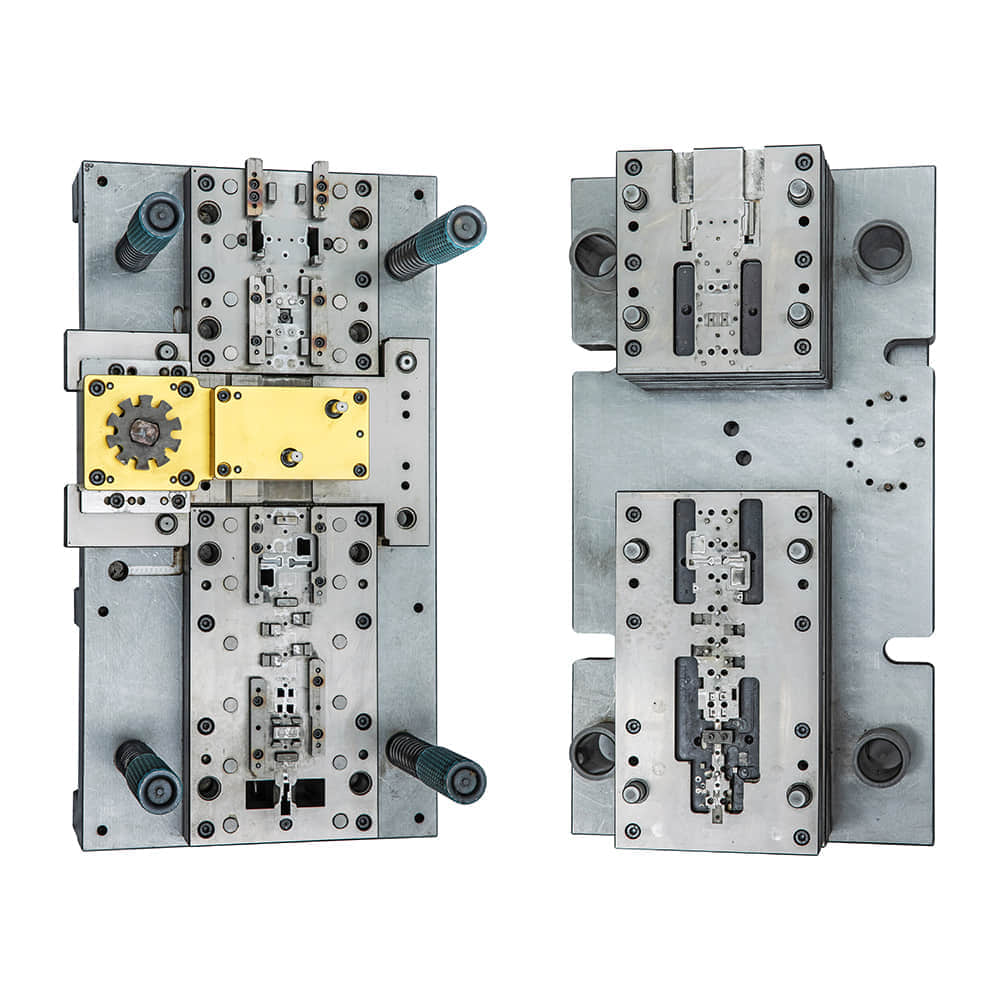
Introduction
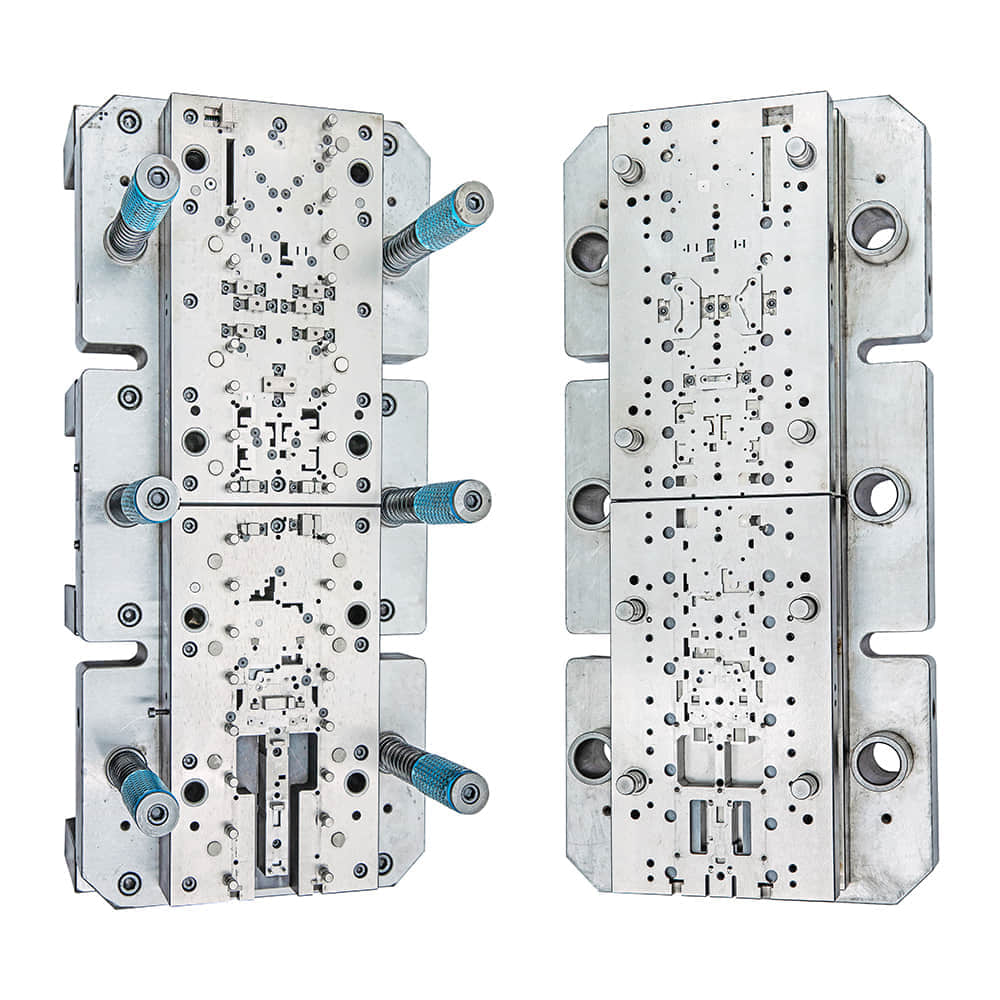
Blanking dies are an integral part of modern manufacturing processes, serving a critical role in various industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, and more. These specialized tools play a pivotal role in shaping raw materials into precise components, facilitating the creation of countless everyday products. In this article, we delve into the world of blanking dies, exploring their mechanics, applications, and significance in today’s industrial landscape.
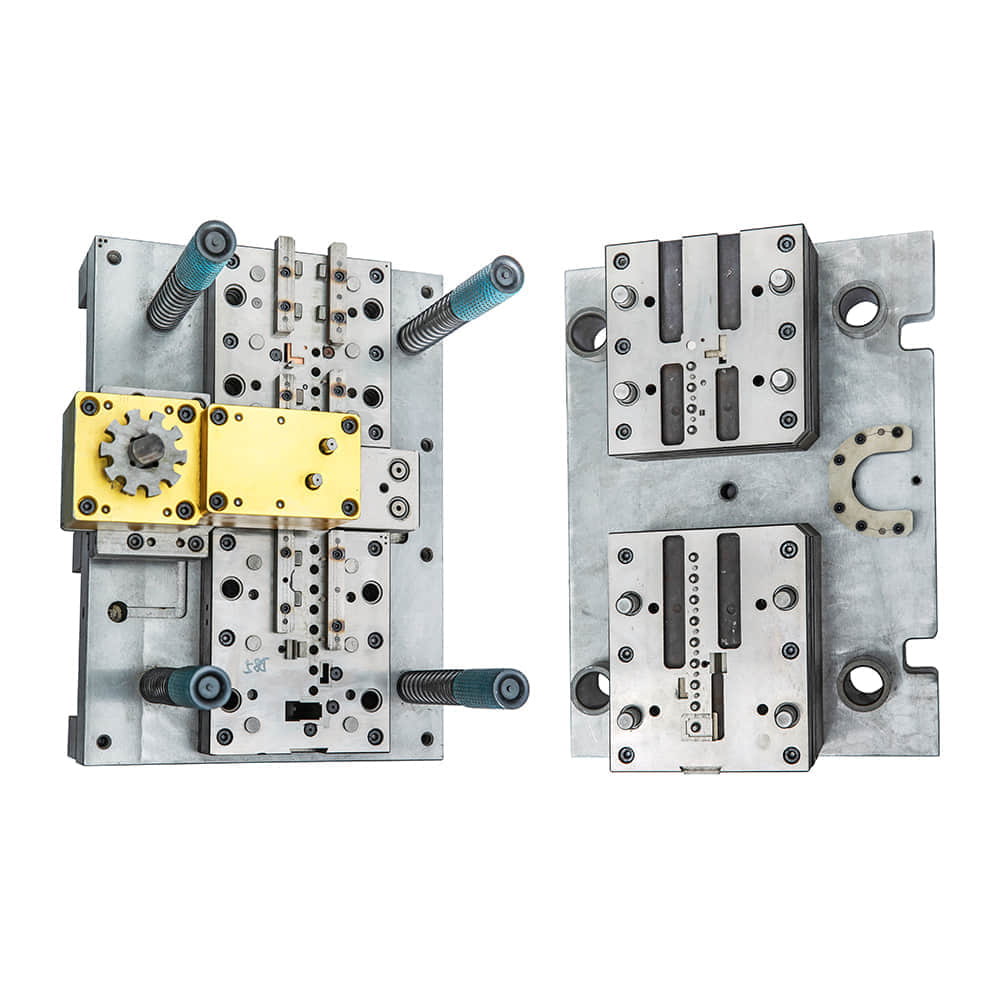
Mechanics of Blanking Dies Blanking dies are tools used to cut out intricate shapes from sheet metal or other flat materials, often in large quantities. The process involves the application of significant force to shear the material along a predetermined cutting line, resulting in a precisely shaped piece known as a “blank.” The mechanics of blanking dies are based on principles of force, material properties, and precision engineering. These dies consist of a punch, which exerts the cutting force, and a die, which provides support for the material being cut. When the punch and die come together, the material experiences plastic deformation and ultimately fractures along the edges of the die aperture. Proper alignment and sharpness of the punch and die are essential for clean and accurate cuts. Factors such as material thickness, hardness, and the complexity of the shape being cut influence the design of the blanking die and the force required. Applications of Blanking Dies The applications of blanking dies are widespread and diverse. One of the primary uses is in the automotive industry, where blanking dies are employed to create intricate components like gears, clutch plates, and engine parts. The electronics sector relies on blanking dies to produce components for gadgets, such as smartphone cases and connectors. Additionally, household appliances, aerospace components, and packaging materials are often manufactured using blanking dies. The efficiency and accuracy of blanking dies make them invaluable for mass production. Their ability to quickly transform raw materials into uniform blanks significantly reduces production time and costs. Furthermore, blanking dies can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and even textiles, showcasing their adaptability and versatility. Significance in Modern Industry The role of blanking dies in modern industry cannot be overstated. Their contributions extend beyond shaping materials; they impact overall product quality, production speed, and cost-effectiveness. The precision of blanking dies ensures that each cut piece adheres to exact specifications, reducing material waste and the need for further processing. As a result, manufacturers can maintain consistent product quality while optimizing resource utilization. Moreover, the use of blanking dies minimizes the reliance on manual labor, leading to enhanced safety for workers and reducing the risk of errors. This automation, coupled with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technologies, enables intricate designs to be executed with remarkable accuracy. Conclusion In conclusion, blanking dies play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing across various industries. Their ability to shape raw materials into precise components with efficiency, accuracy, and consistency has revolutionized the way products are produced. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that blanking dies will evolve further, becoming even more sophisticated and adaptable to the ever-changing demands of industry. Whether in the creation of automotive parts, electronics, or everyday items, blanking dies remain at the forefront of innovation, driving progress and shaping the world around us.