Relays are essential components in electrical circuits, used to control the flow of current in various systems. They act as electrically operated switches, enabling control over high-power circuits with low-power signals. As the demand for more efficient, durable, and versatile relays increases, it’s crucial to compare different types of relays to determine the best fit for specific applications. This article presents a comprehensive relay comparison, focusing on key factors such as technical specifications, performance, cost-effectiveness, and reliability.
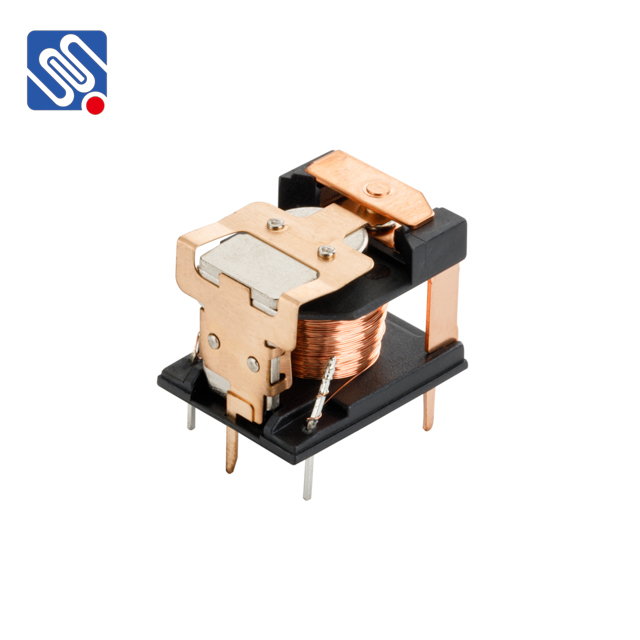
1. Types of Relays and Their Applications Before diving into the comparison, it’s essential to understand the different types of relays. The most common relays include: Electromechanical Relays (EMRs): These relays operate using an electromagnet to move a mechanical switch. They are widely used in industrial and automotive applications due to their simple design and high switching capacity. Solid-State Relays (SSRs): Unlike EMRs, solid-state relays rely on semiconductor components to perform the switching operation. They are typically used in high-speed applications and where durability is a top priority, as they lack moving parts.