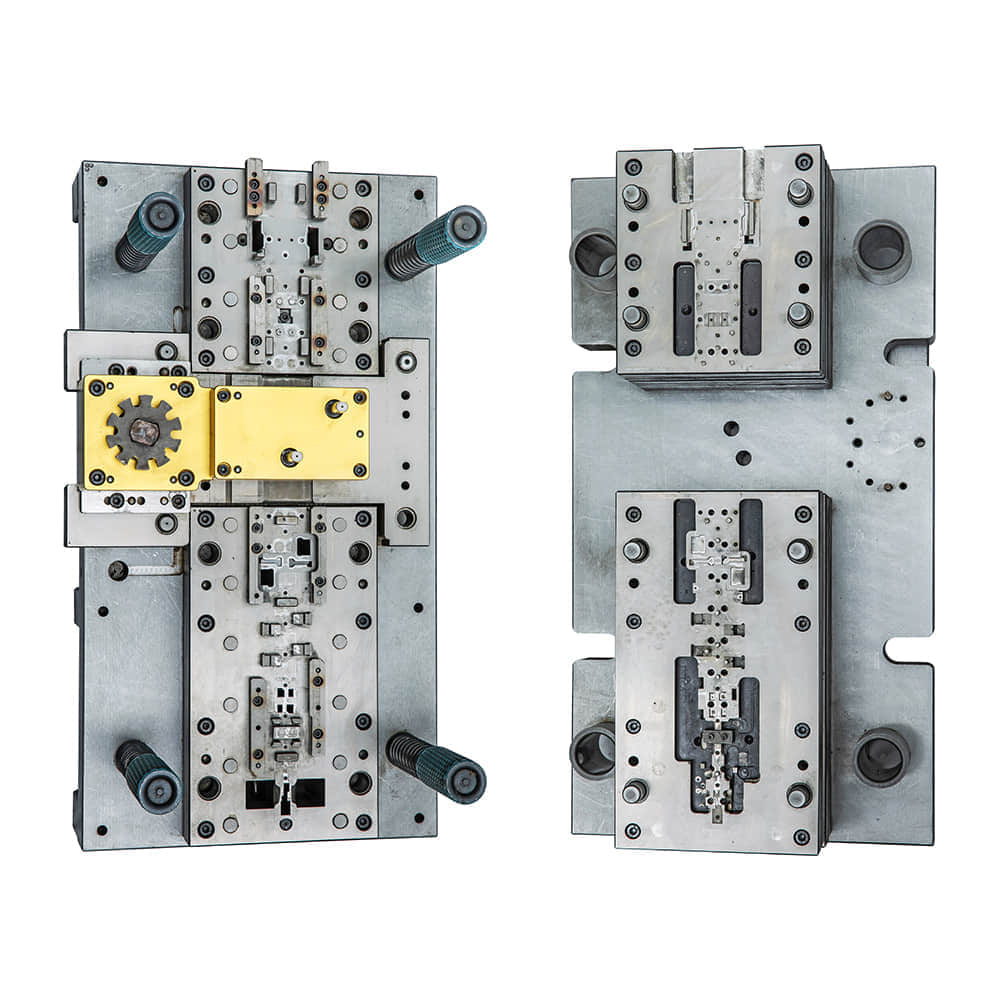
Blanking die, a fundamental tool in the realm of manufacturing, stands as a testament to precision engineering and operational efficiency. This intricate device plays a crucial role in various industries, shaping raw materials into precise components that drive modern technology. In this article, we delve into the world of blanking die, exploring its mechanics, applications, and the impact it has on our daily lives.
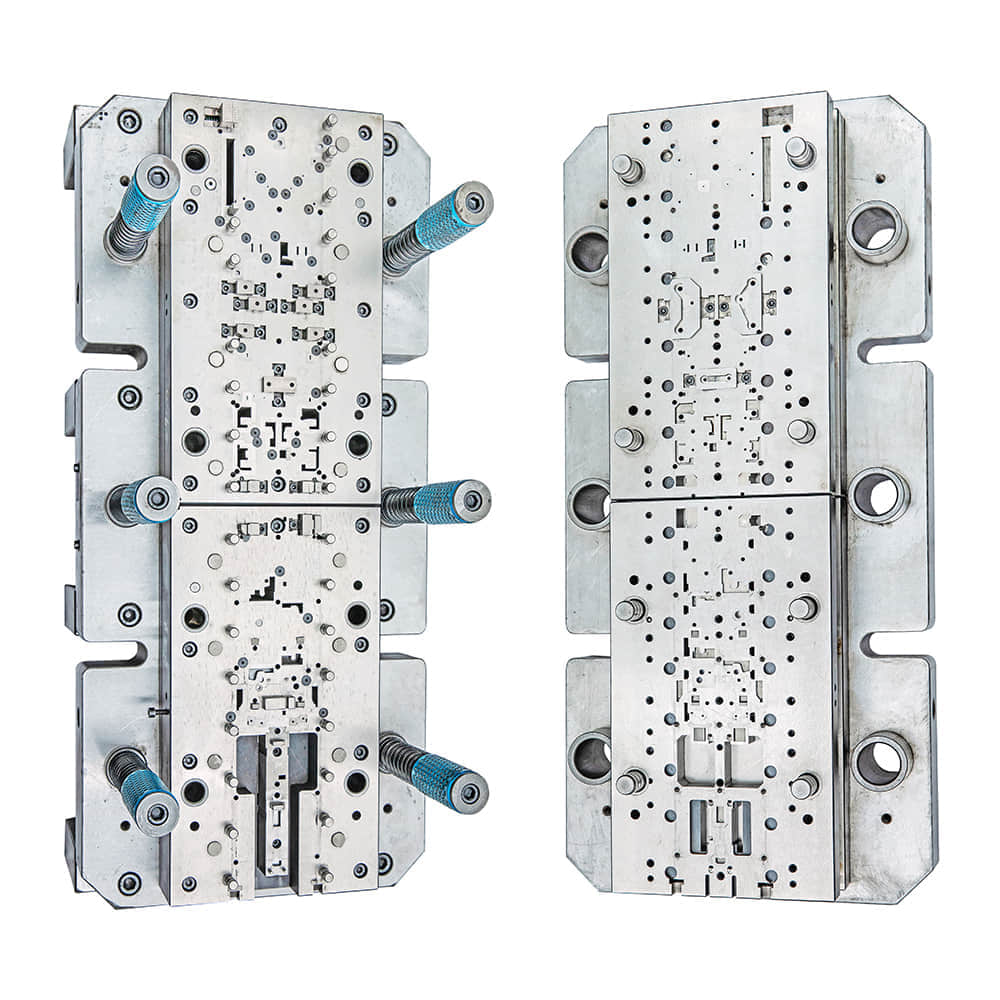
Mechanics and Functionality
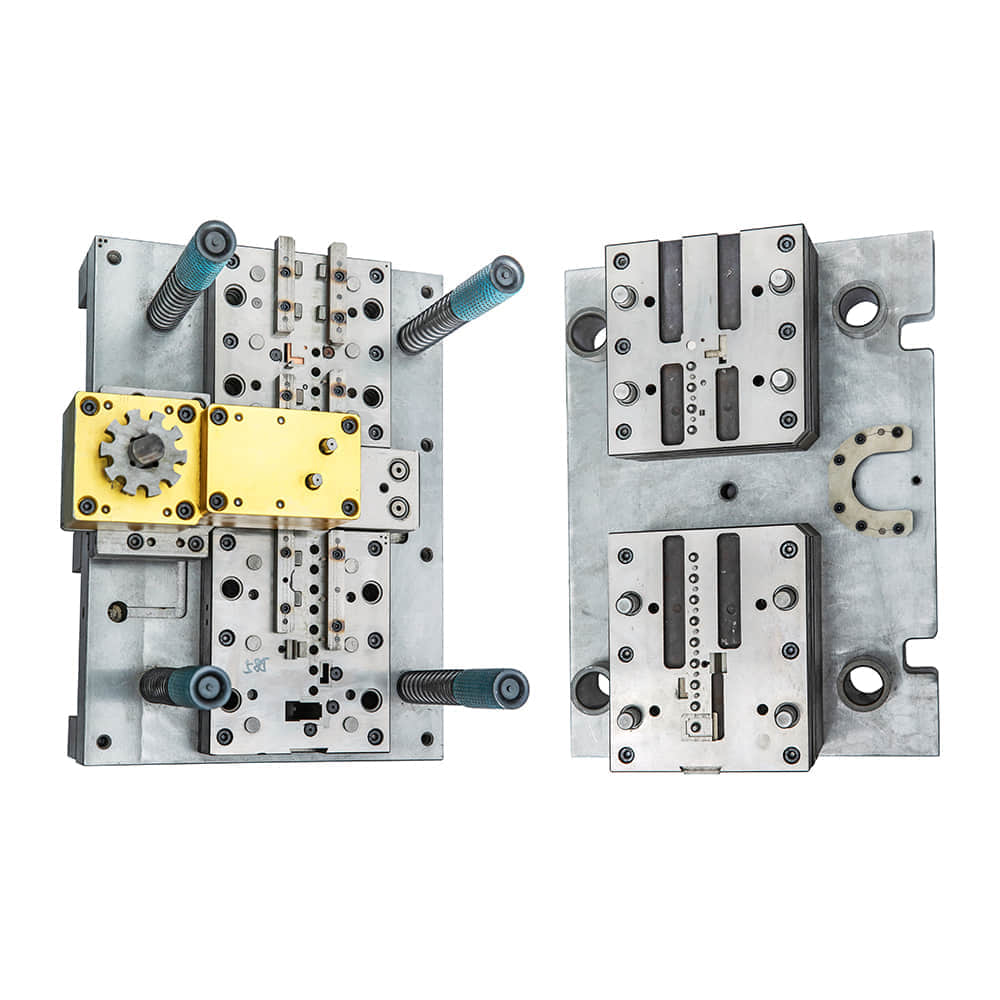
At its core, a blanking die is a specialized tool used for cutting and shaping sheet metal or other materials into desired shapes with incredible precision. The process involves the use of a press to force the die through the material, effectively “blanking” out the desired shape. The die itself consists of two parts: the punch, which is the protruding part, and the die block, which has a hole matching the shape of the punch. When the punch and die block come together, the material placed between them is sheared, creating the intended product. Types of Blanking Die Blanking die techniques have evolved over time to suit a variety of applications. The basic types include: Compound Die: This type of die performs multiple operations in a single press stroke, making it highly efficient for mass production of simple parts. Progressive Die: Ideal for more complex parts, progressive die operations are carried out in a sequence of press strokes, with the workpiece gradually taking its final shape. Combination Die: As the name suggests, this type combines both blanking and forming operations in a single stroke, minimizing the need for multiple setups. Piercing Die: While similar to blanking, this die focuses on creating holes in the workpiece, rather than cutting out the entire shape. Applications in Diverse Industries Blanking dies find applications in a myriad of industries, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, and consumer goods. In the automotive sector, these dies are responsible for shaping intricate parts such as gears, engine components, and body panels. In electronics, the delicate precision of blanking dies is crucial for crafting intricate components found in devices ranging from smartphones to complex circuitry. Moreover, blanking dies play a vital role in the aerospace industry, where the demand for lightweight yet robust components necessitates accurate shaping of advanced materials. Even in everyday products like household appliances and packaging, blanking dies enable the creation of precise shapes that fit seamlessly into our lives. The Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency One of the most significant advantages of blanking dies lies in their contribution to manufacturing efficiency. The precision and repeatability of the die-cutting process ensure minimal material waste and consistent quality in each produced piece. This not only reduces costs but also accelerates production timelines, meeting the demands of a fast-paced market. Challenges and Innovations While blanking die technology has come a long way, challenges persist. The intricate nature of some parts demands the utmost precision, pushing engineers to explore innovative solutions. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technologies have revolutionized the design and production process, allowing for virtual simulations before the physical die is even created. Furthermore, advancements in materials science have led to the development of new tooling materials that enhance durability and precision. High-speed steel, carbide, and various coatings extend the lifespan of dies, enabling longer production runs without sacrificing quality. Conclusion The blanking die is more than just a manufacturing tool; it’s a testament to human ingenuity and engineering excellence. Its ability to shape raw materials into intricate components with unparalleled precision and efficiency has elevated industries across the globe. From the creation of cutting-edge automotive parts to the delicate inner workings of electronic devices, blanking dies continue to shape the world around us, one precise cut at a time.