Relay comparison, though a simple phrase, spans across various domains such as electronics, telecommunications, sports, and even business processes. Understanding the nuances of relay comparison requires diving into these different fields and examining how relays function, their importance, and how different models or methods are evaluated against each other. In this article, we will explore relay comparison across three key areas: electronics, telecommunications, and sports, highlighting their significance and the factors influencing the comparisons.
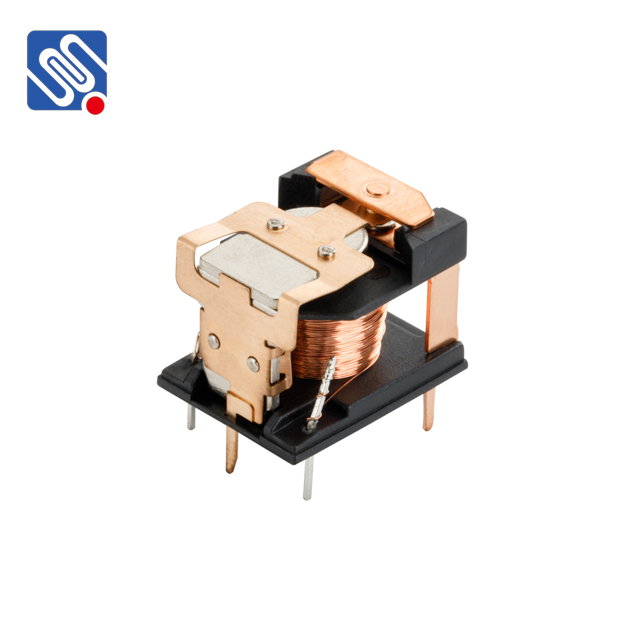
Relay Comparison in Electronics In the world of electronics and electrical engineering, a relay is an electromagnetic switch used to control the flow of electricity in a circuit. It allows a small electrical signal to control a larger current or voltage, making it an essential component in a wide range of applications from automotive systems to industrial machinery. The most common relay types include electromagnetic, solid-state, and thermal relays. Each type has its advantages and limitations, and a relay comparison typically involves analyzing parameters such as switching speed, current and voltage rating, power consumption, and durability. For instance, solid-state relays, which use semiconductor components instead of mechanical parts, are faster and more reliable than traditional electromagnetic relays, but they tend to be more expensive.