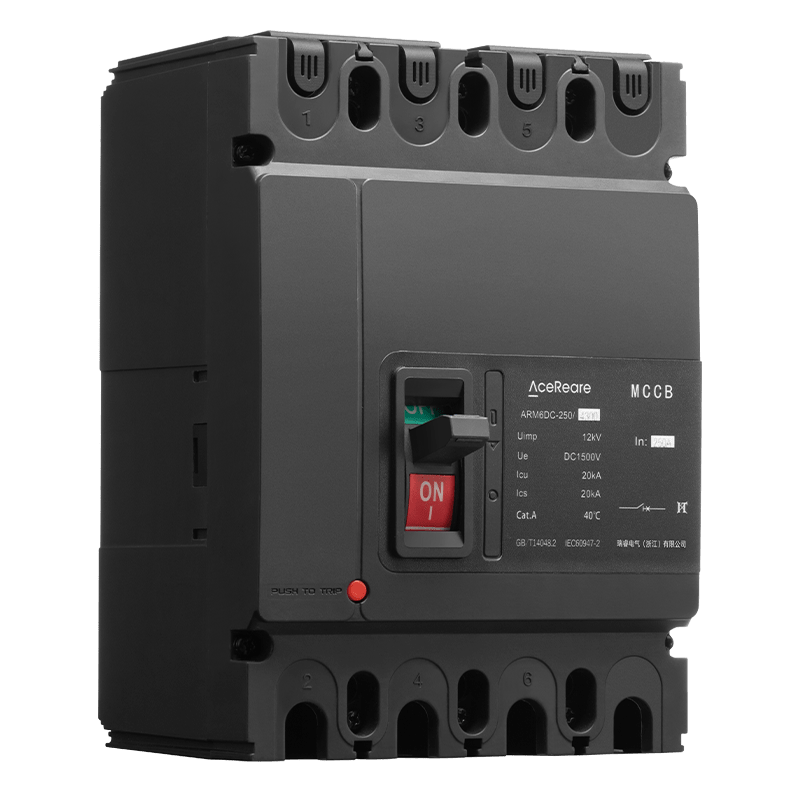
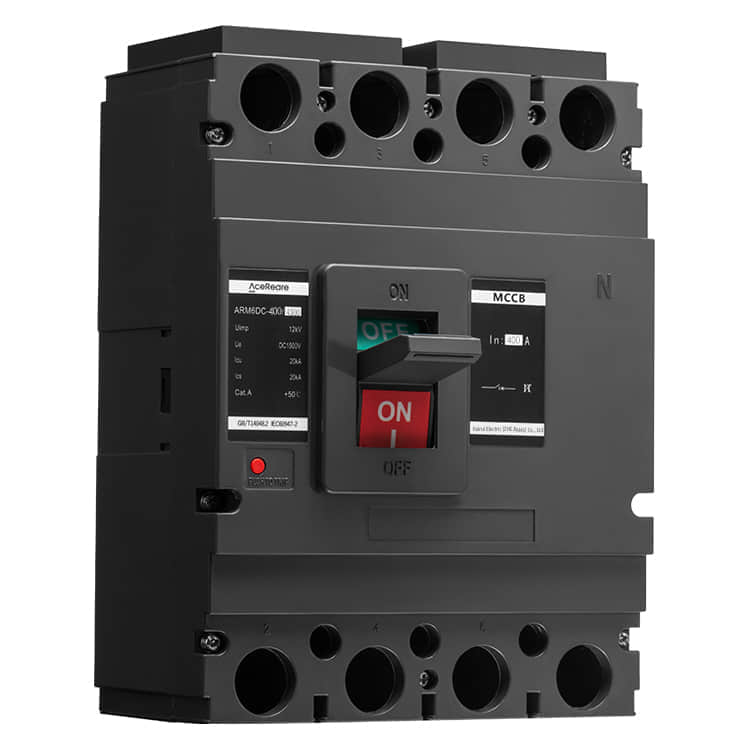
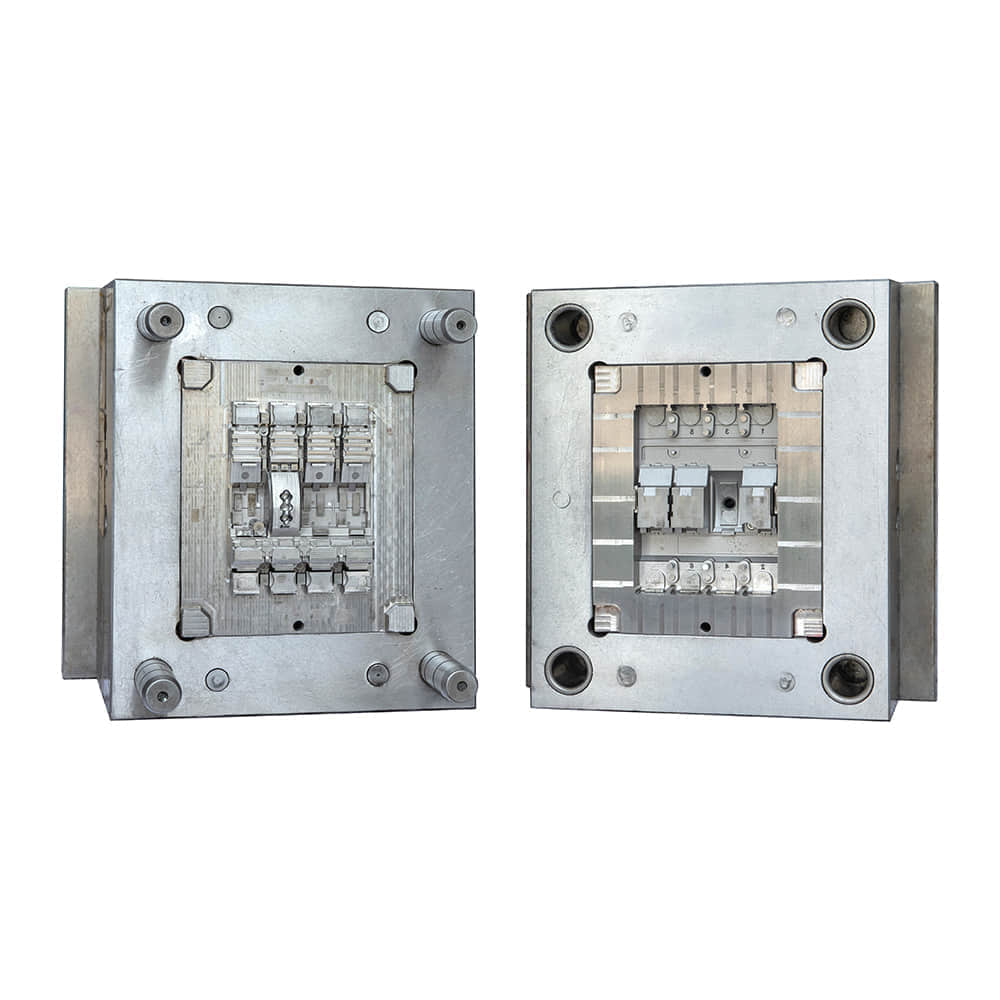
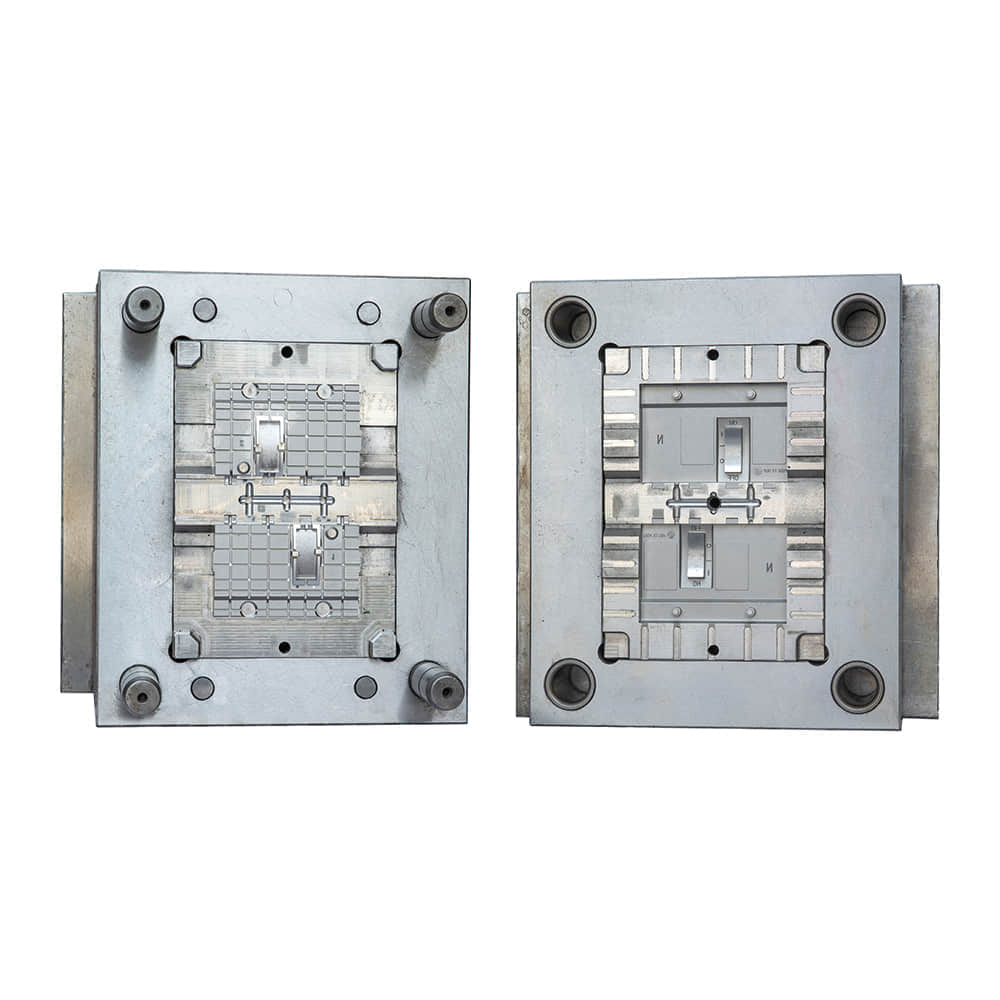
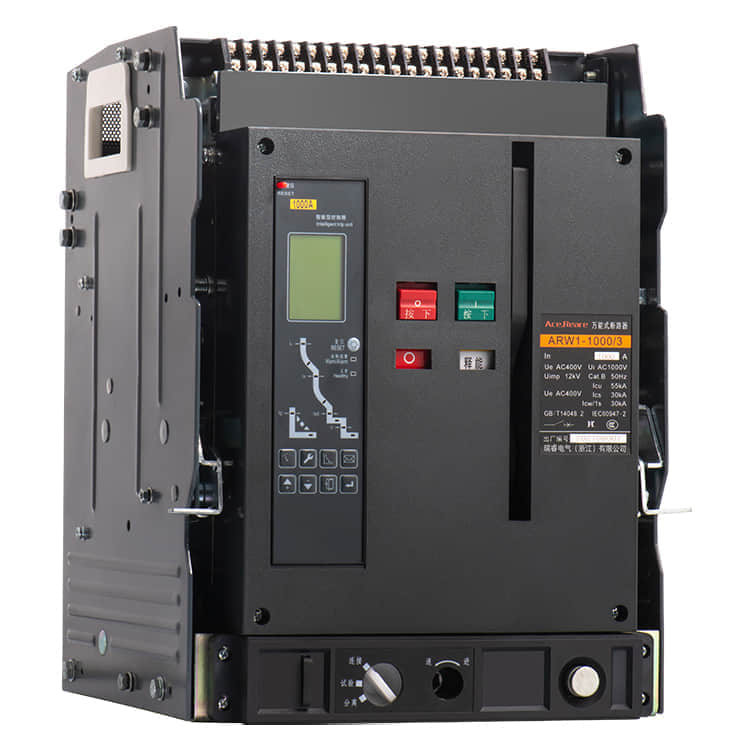
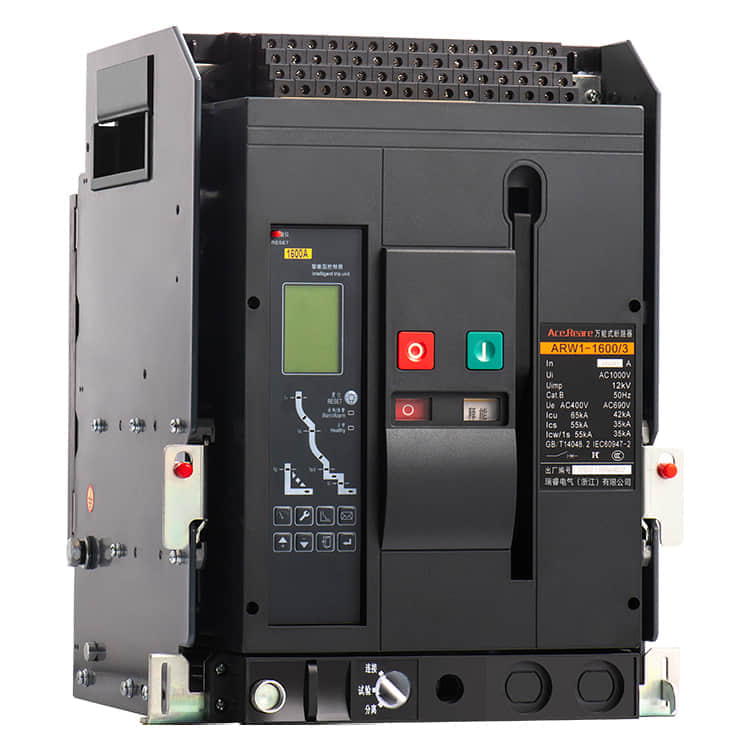
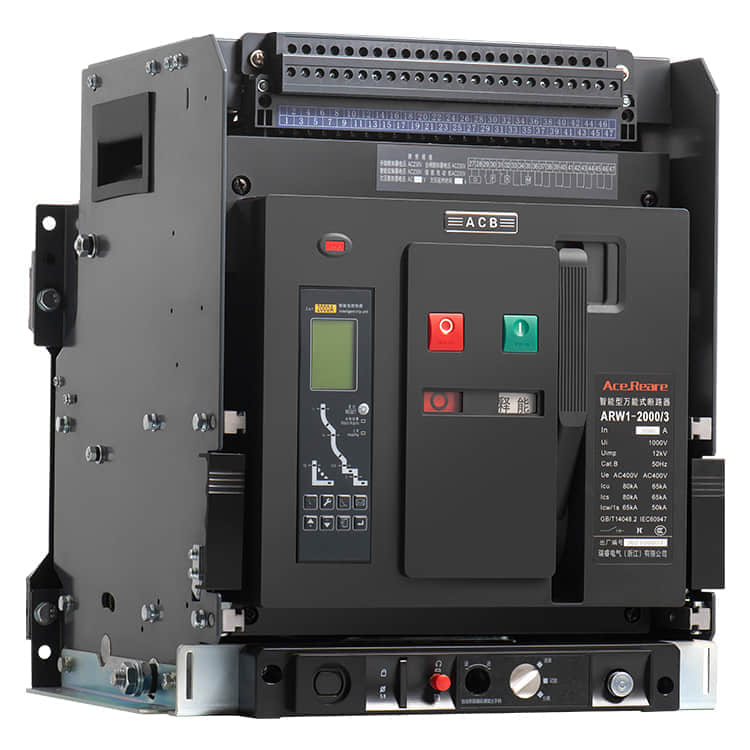
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) are vital components in electrical systems, serving as guardians of safety and efficiency. These devices are designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrents and short circuits, preventing fires and equipment damage. Behind the scenes of this critical electrical component, there are manufacturers who play a pivotal role in ensuring that our homes, industries, and institutions are powered safely and reliably. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of MCCB manufacturing, shedding light on the processes and innovations that make these devices the unsung heroes of modern electrical systems.
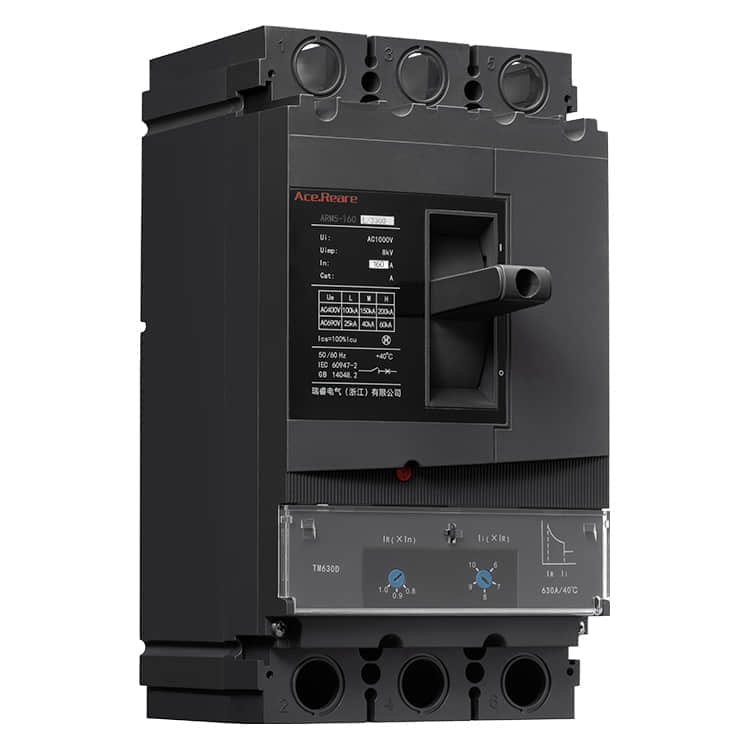

The Heart of MCCB Manufacturing
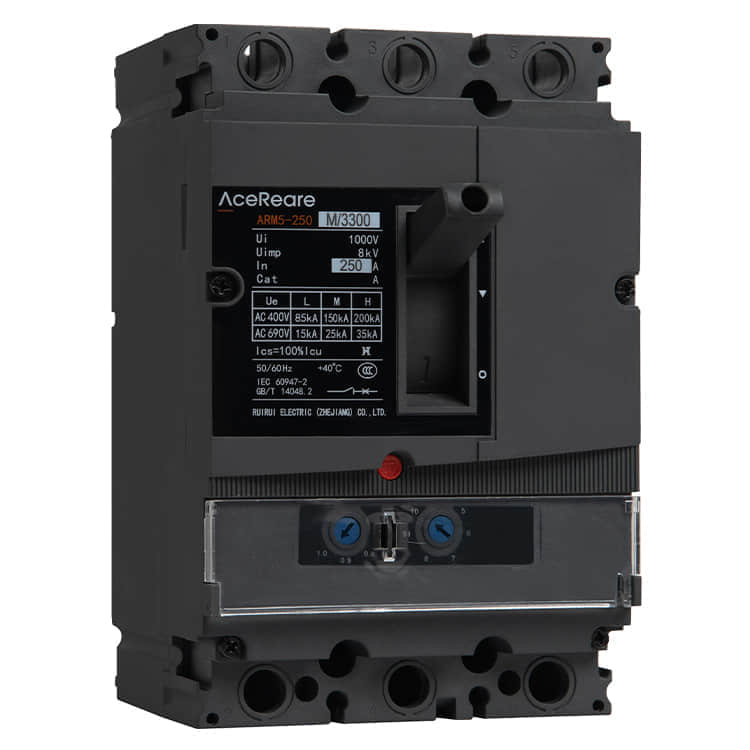

MCCBs are complex pieces of engineering that require precision, expertise, and unwavering commitment to quality. Manufacturers of MCCBs must carefully select materials, design circuitry, and ensure that every component meets stringent safety and performance standards. Material Selection One of the first steps in MCCB manufacturing is the selection of materials. Housing materials, such as high-impact thermoset plastics, are chosen for their ability to withstand heat and impact. Internal components, including conductive elements, must possess excellent electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. Manufacturers often collaborate with material scientists to develop specialized compounds that can meet these demanding requirements. Precision Engineering The engineering behind MCCBs is a blend of electrical and mechanical expertise. Circuitry must be designed to handle a wide range of current ratings, and it must do so with precision to avoid nuisance tripping or catastrophic failures. This is achieved through the use of advanced simulation and modeling techniques, ensuring that MCCBs respond accurately to different fault conditions. Stringent Testing Safety is paramount in MCCB manufacturing. Every device must undergo rigorous testing to ensure it meets industry standards and certifications. This includes thermal testing, short-circuit testing, and endurance testing, among others. MCCB manufacturers invest heavily in state-of-the-art testing facilities to guarantee that their products can handle the harshest conditions without compromise. Innovations Driving MCCB Manufacturing In recent years, MCCB manufacturers have embraced innovation to improve the performance and functionality of their products. Here are some key innovations shaping the MCCB manufacturing landscape: Digital Connectivity The integration of digital technologies into MCCBs has revolutionized their capabilities. Smart MCCBs can communicate real-time data on power consumption, fault conditions, and maintenance needs, enabling more proactive and efficient management of electrical systems. This not only enhances safety but also contributes to energy efficiency. Arc Flash Mitigation Arc flashes are a significant hazard in electrical systems. MCCB manufacturers have developed advanced arc flash mitigation technologies that reduce the severity of arc flash incidents, protecting both equipment and personnel. These innovations are a testament to the commitment to safety within the industry. Compact Designs Space is often at a premium in electrical panels. MCCB manufacturers have responded by developing more compact and space-efficient designs without compromising performance. This innovation is particularly valuable in retrofitting older systems with modern MCCBs. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices In today’s environmentally conscious world, MCCB manufacturers are also focusing on sustainable practices. They are working towards reducing the environmental footprint of their operations by recycling materials, optimizing energy usage, and minimizing waste. Conclusion The manufacturers of Molded Case Circuit Breakers are unsung heroes in the world of electrical safety. Their commitment to precision engineering, rigorous testing, and continuous innovation ensures that electrical systems around the world run safely and efficiently. As technology advances, so too will the capabilities of MCCBs, making them even more reliable and integral to our daily lives. So, the next time you flip a switch or plug in a device, remember the manufacturers behind the scenes, working tirelessly to keep you safe and powered up.