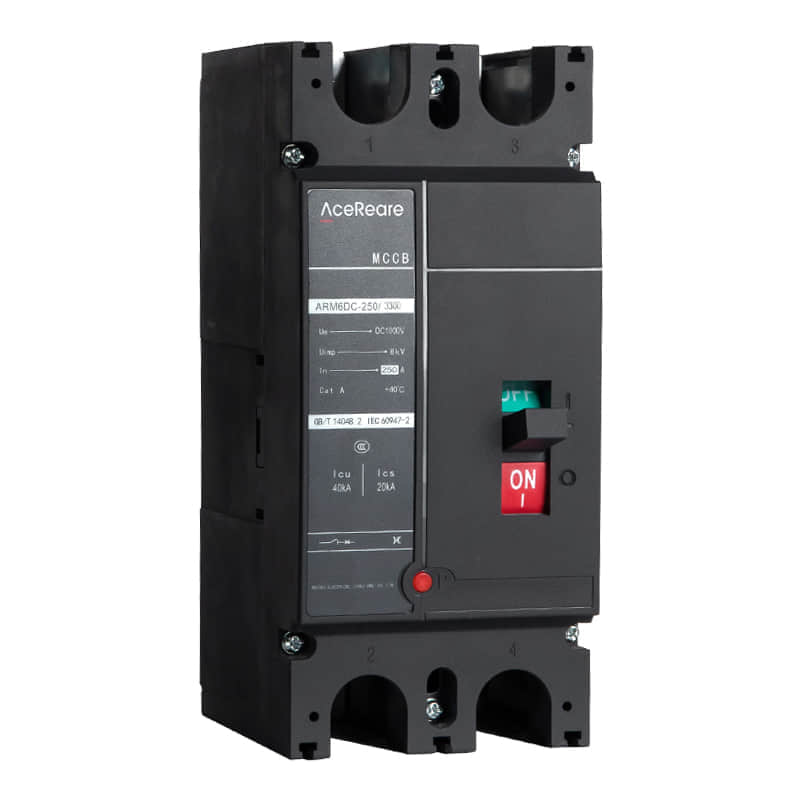
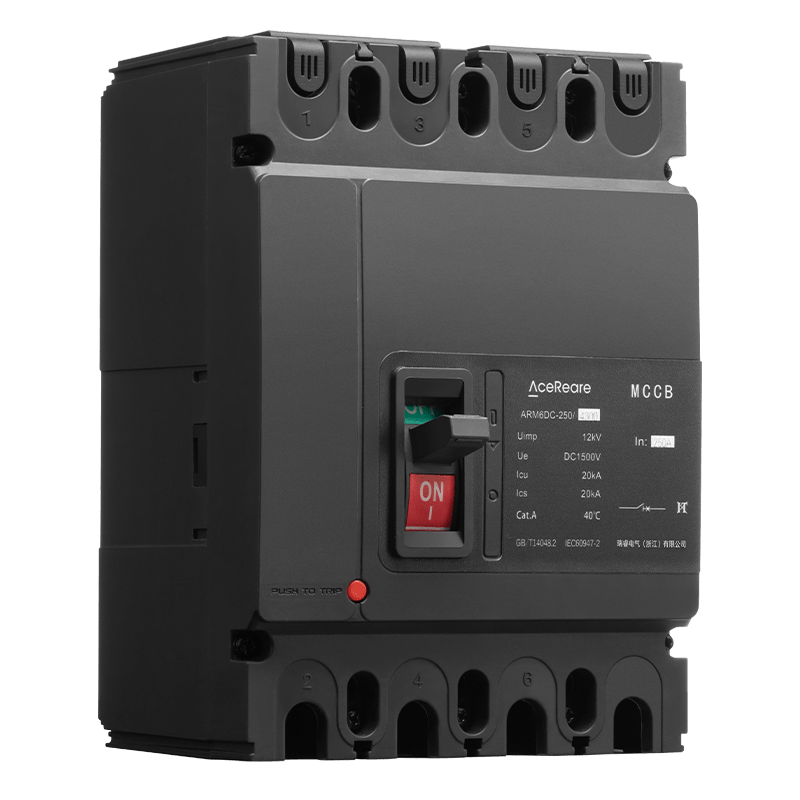
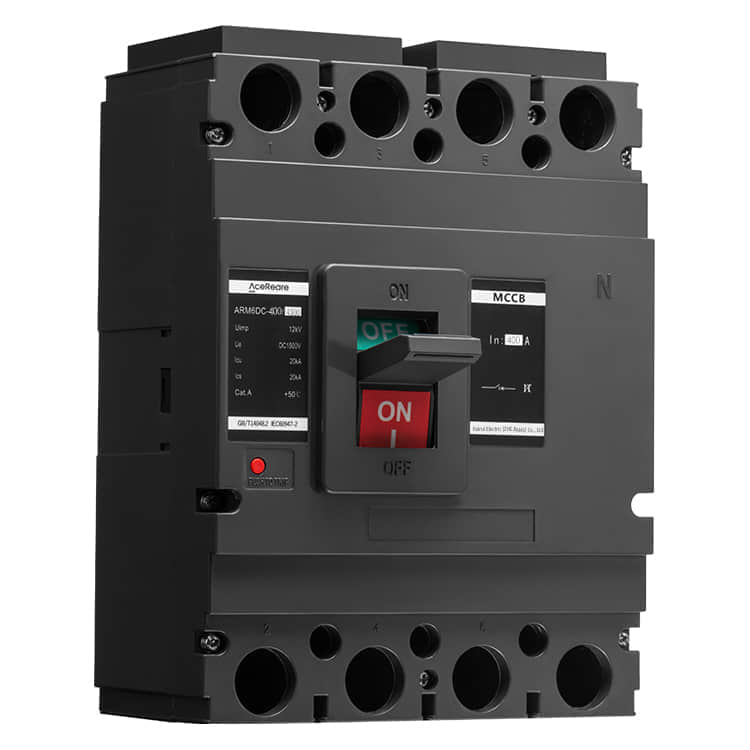
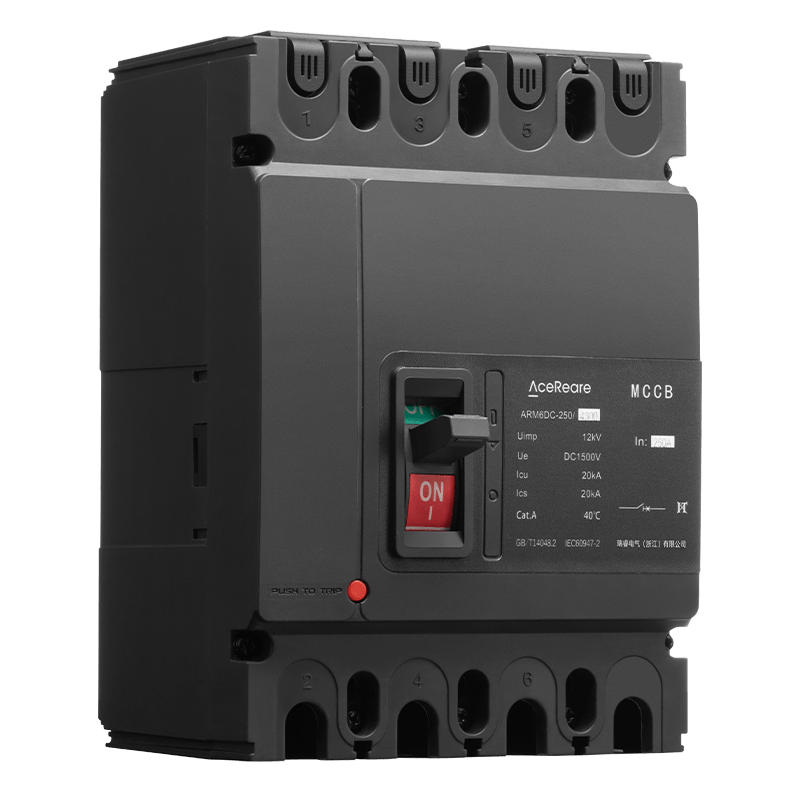
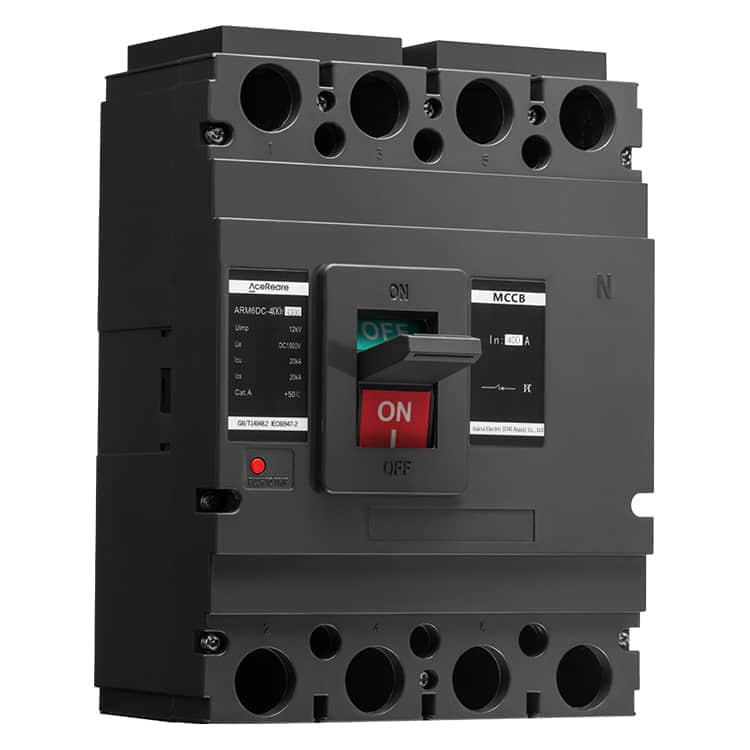
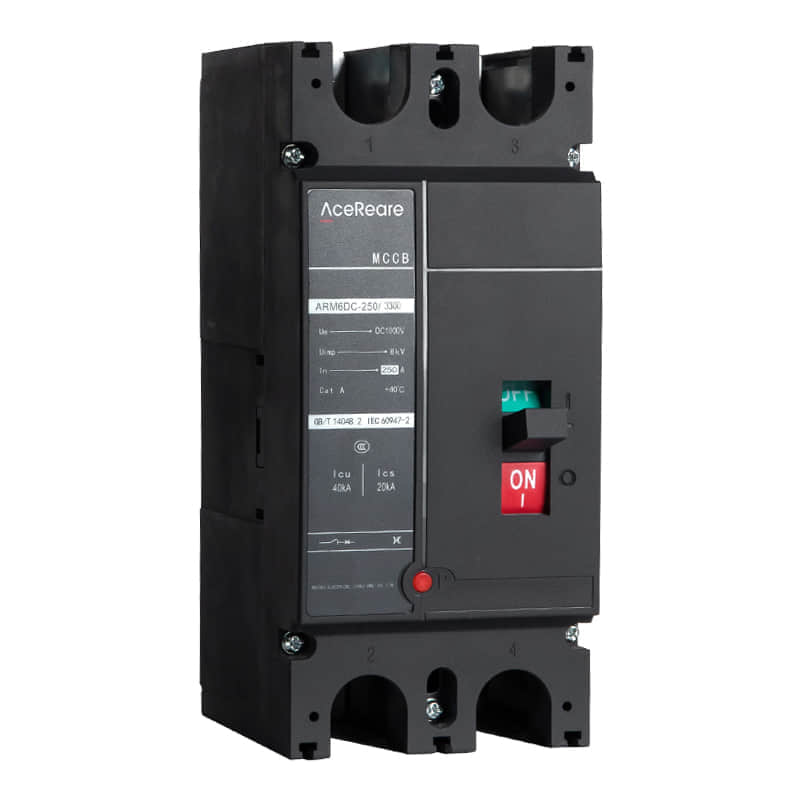
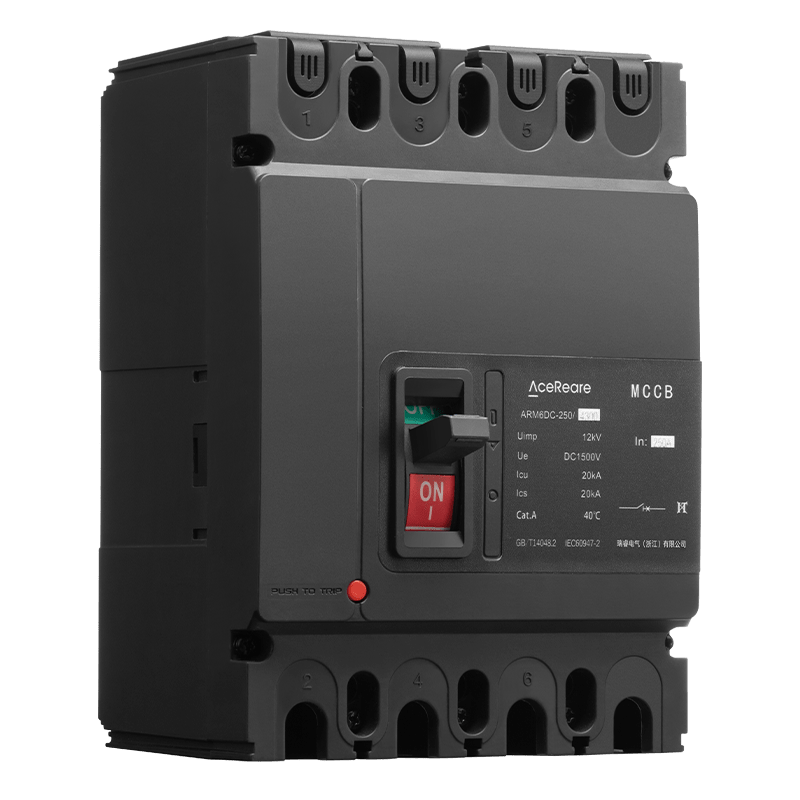
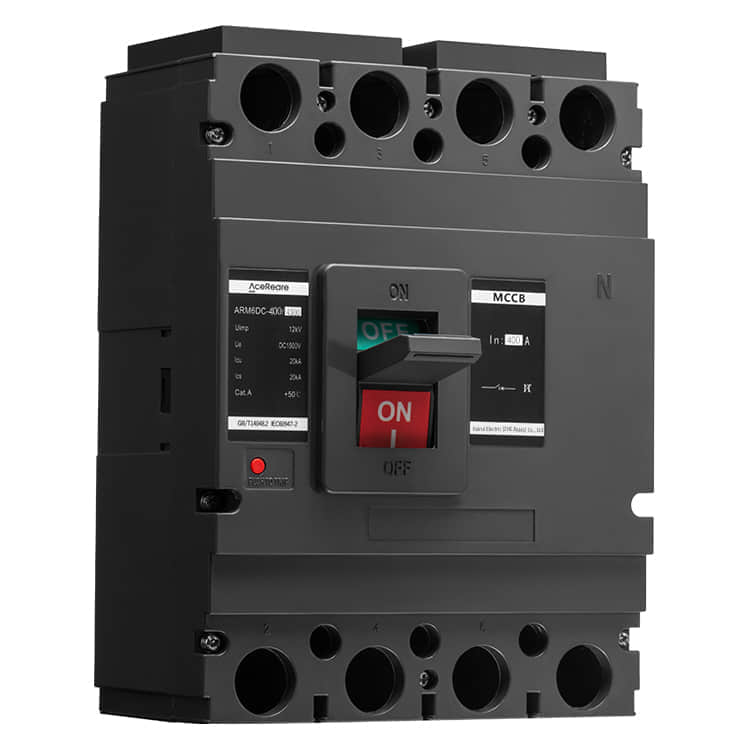
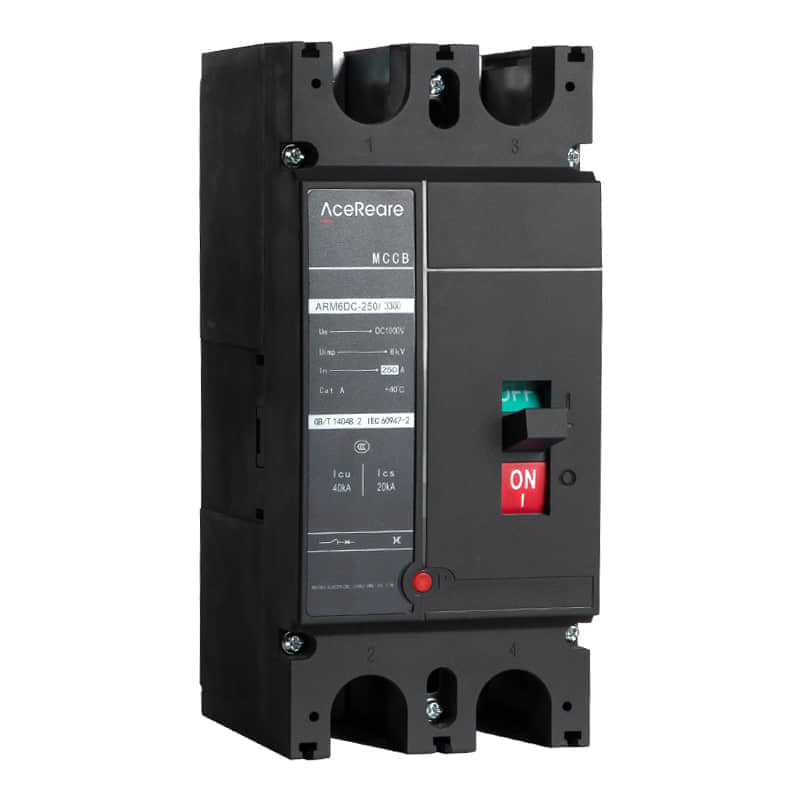
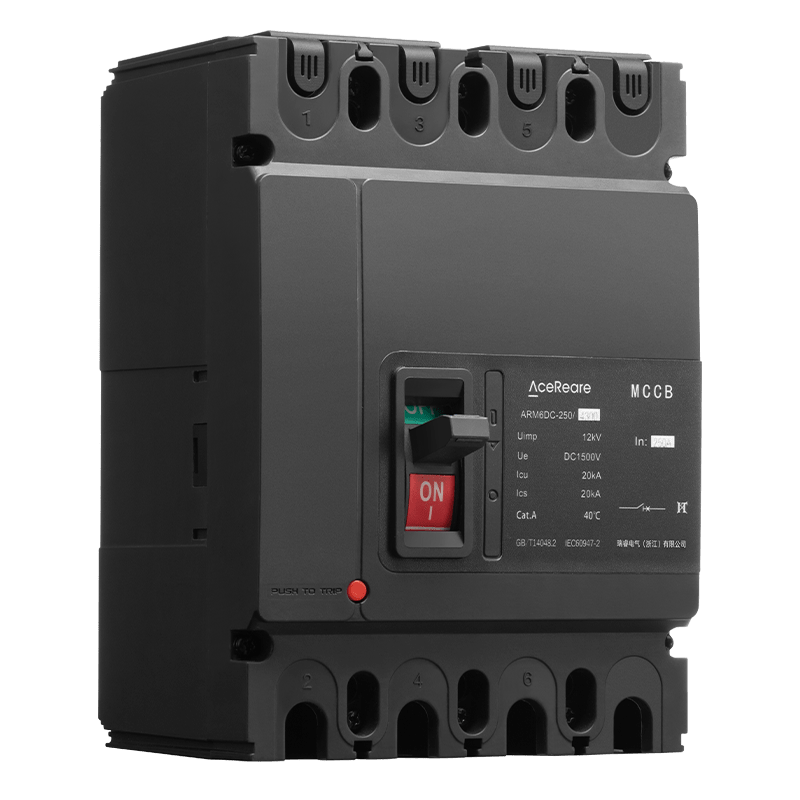
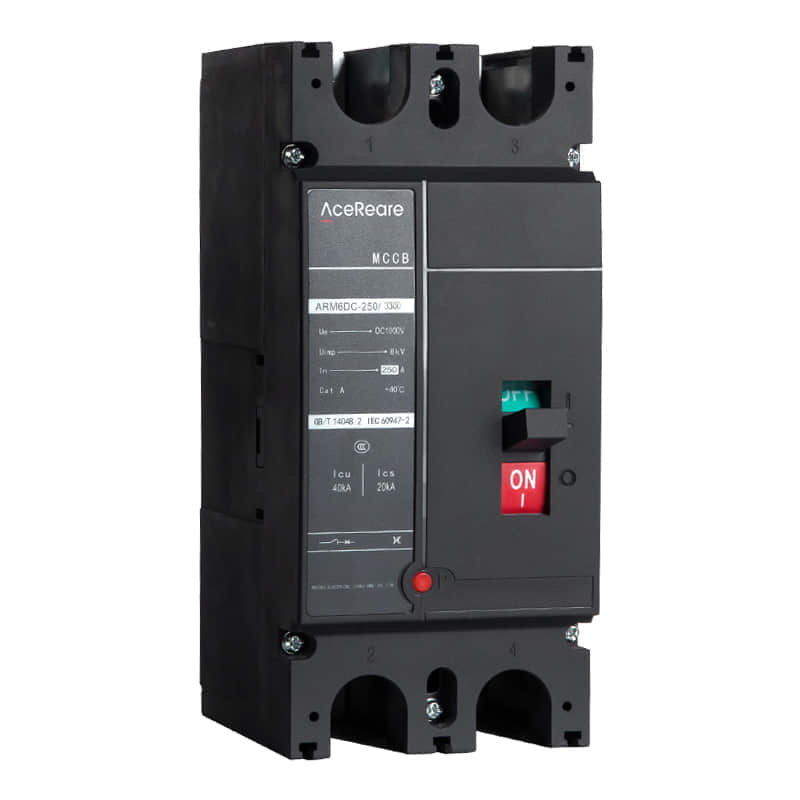
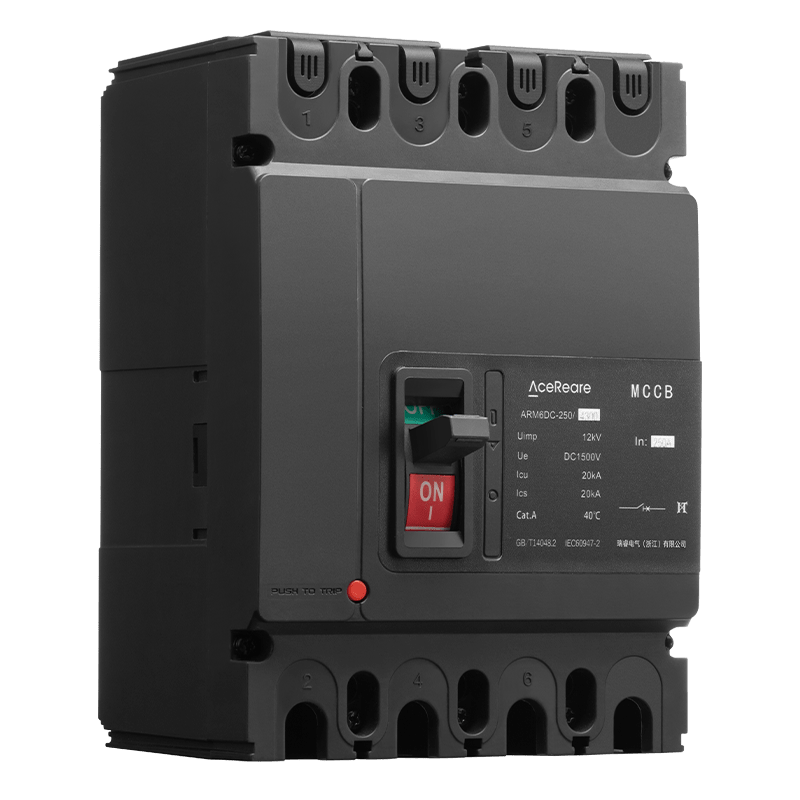
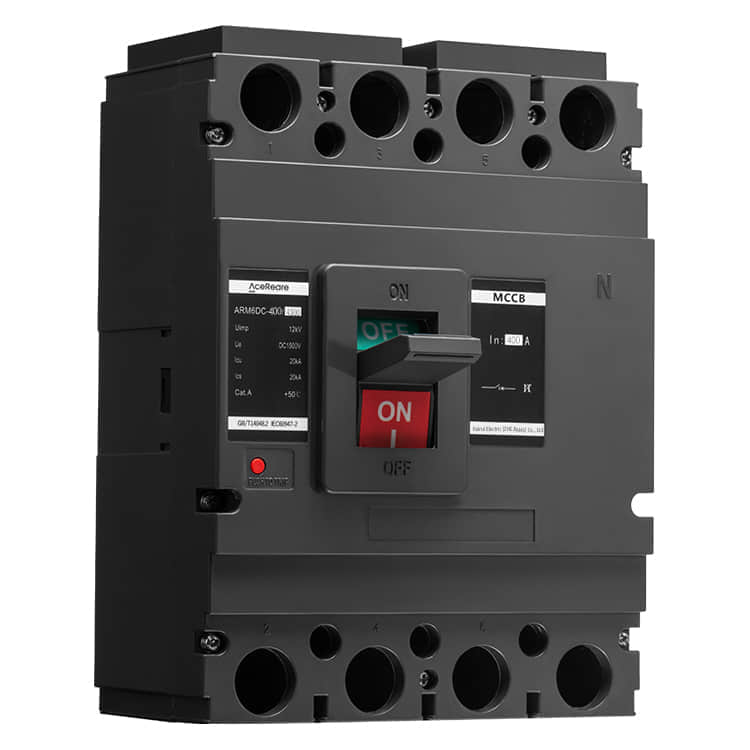
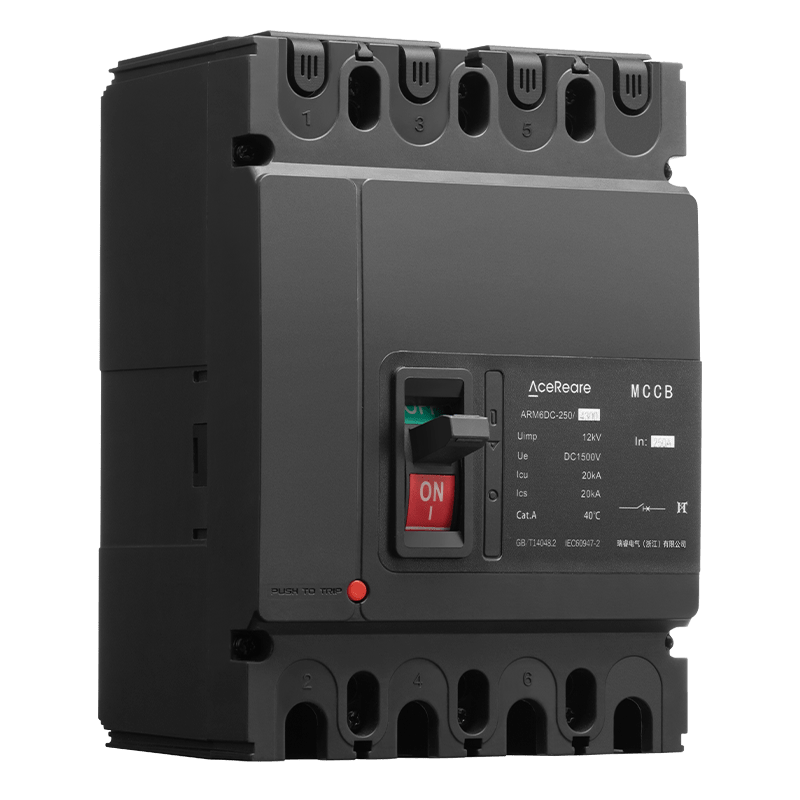
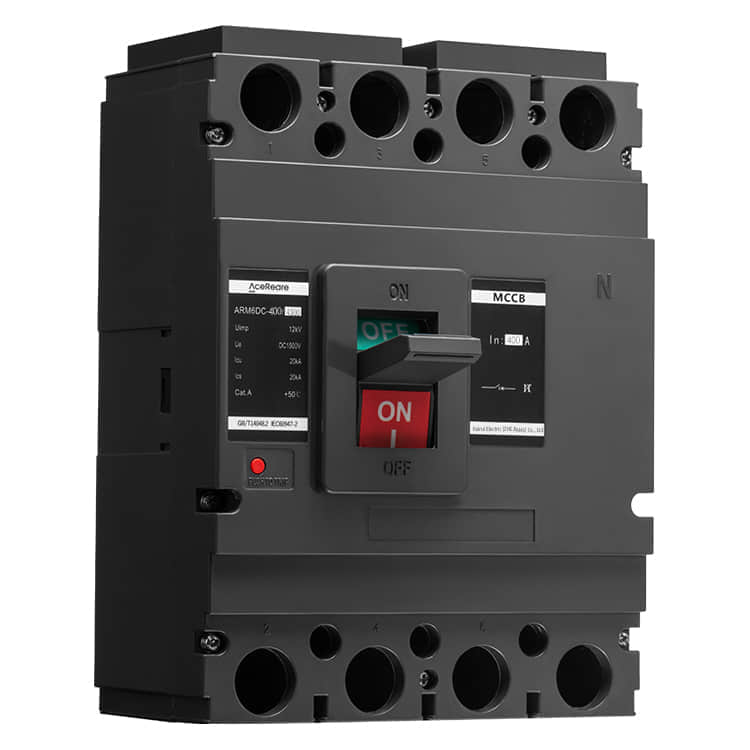
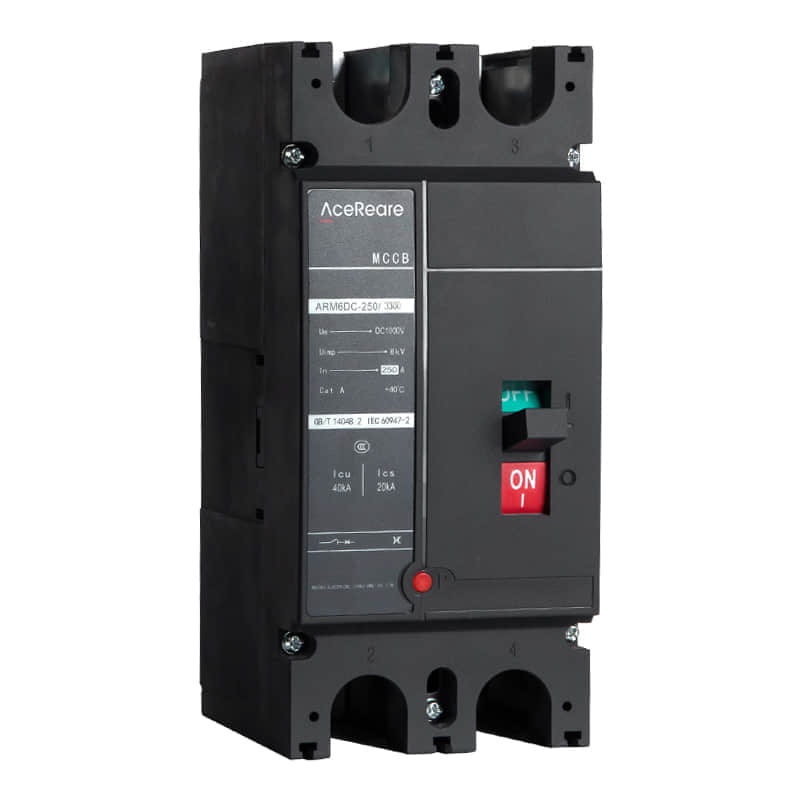
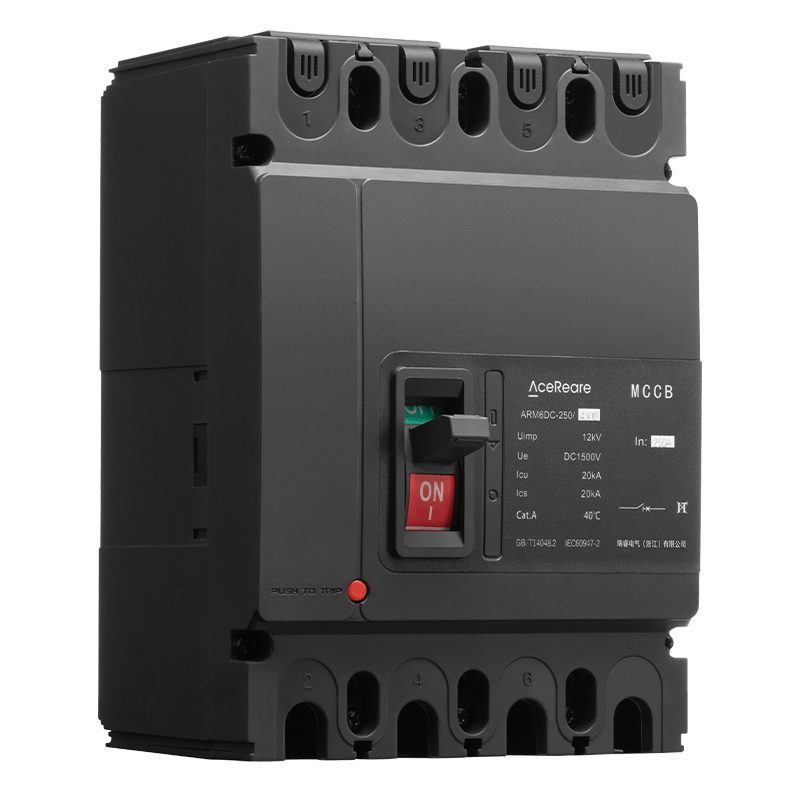
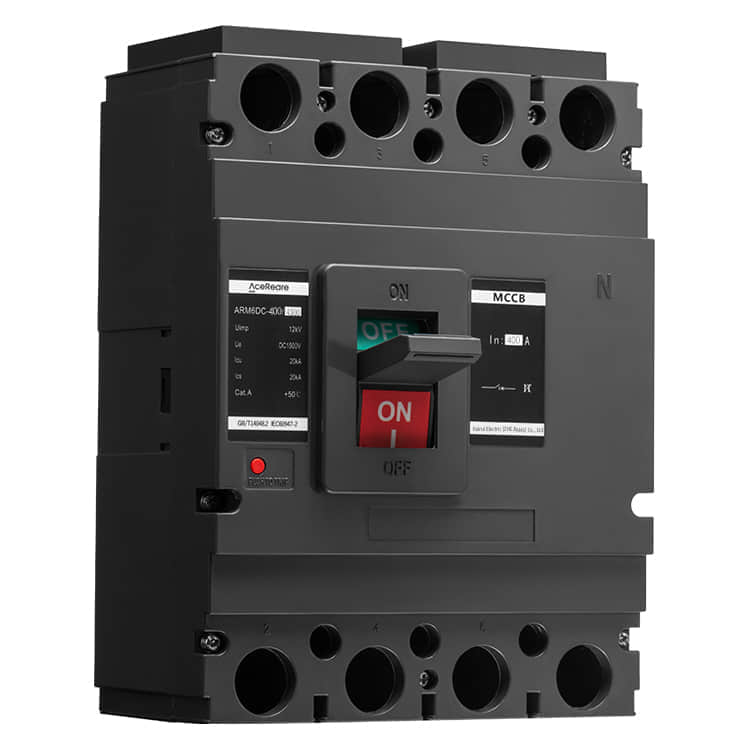
In the realm of modern manufacturing, Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) molding has emerged as a revolutionary process that combines the benefits of traditional molding techniques with innovative materials and technology. SMC molding, known for its versatility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, has found applications in various industries, reshaping the way we approach production.
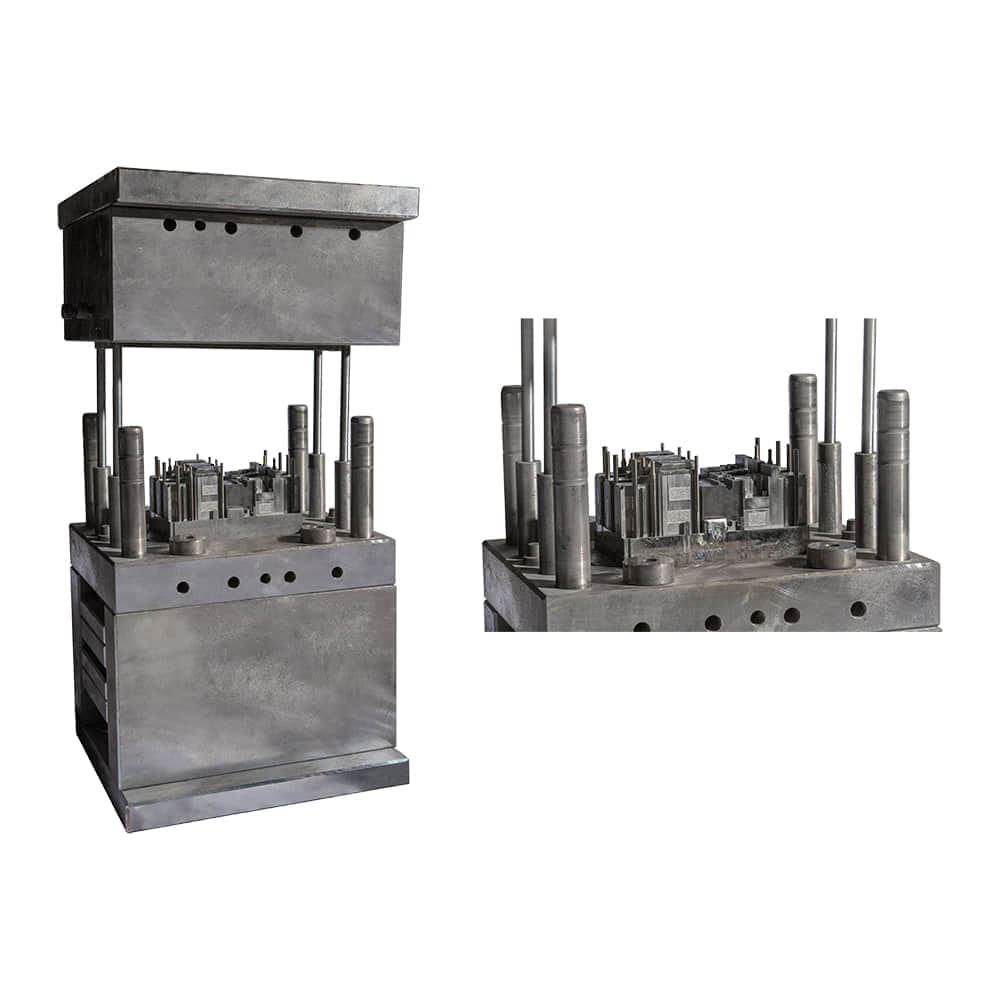

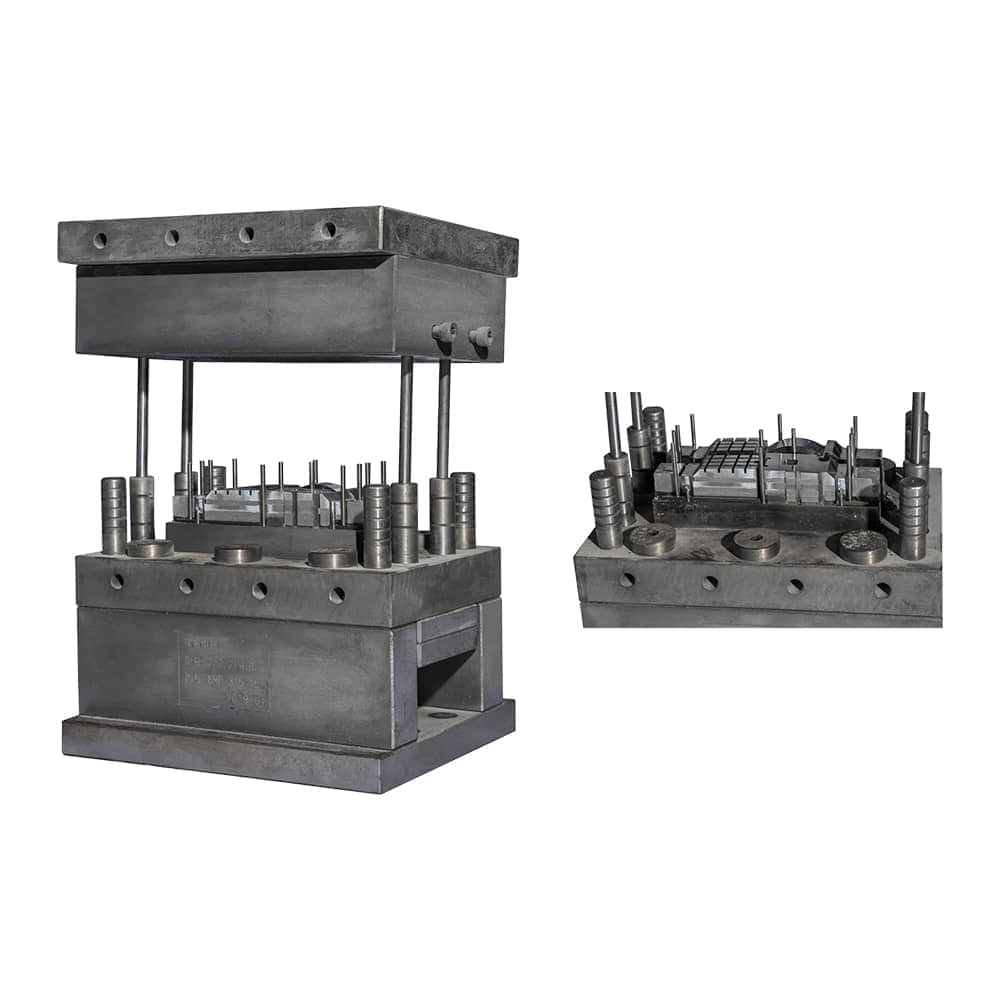
SMC molding involves the compression molding of a reinforced composite material known as Sheet Molding Compound. This compound comprises chopped glass fibers, thermosetting resin, and additives. The process begins with the careful layering of the SMC into a mold cavity, followed by the application of heat and pressure. As the material cures, it takes on the desired shape, resulting in a final product that boasts impressive mechanical properties.
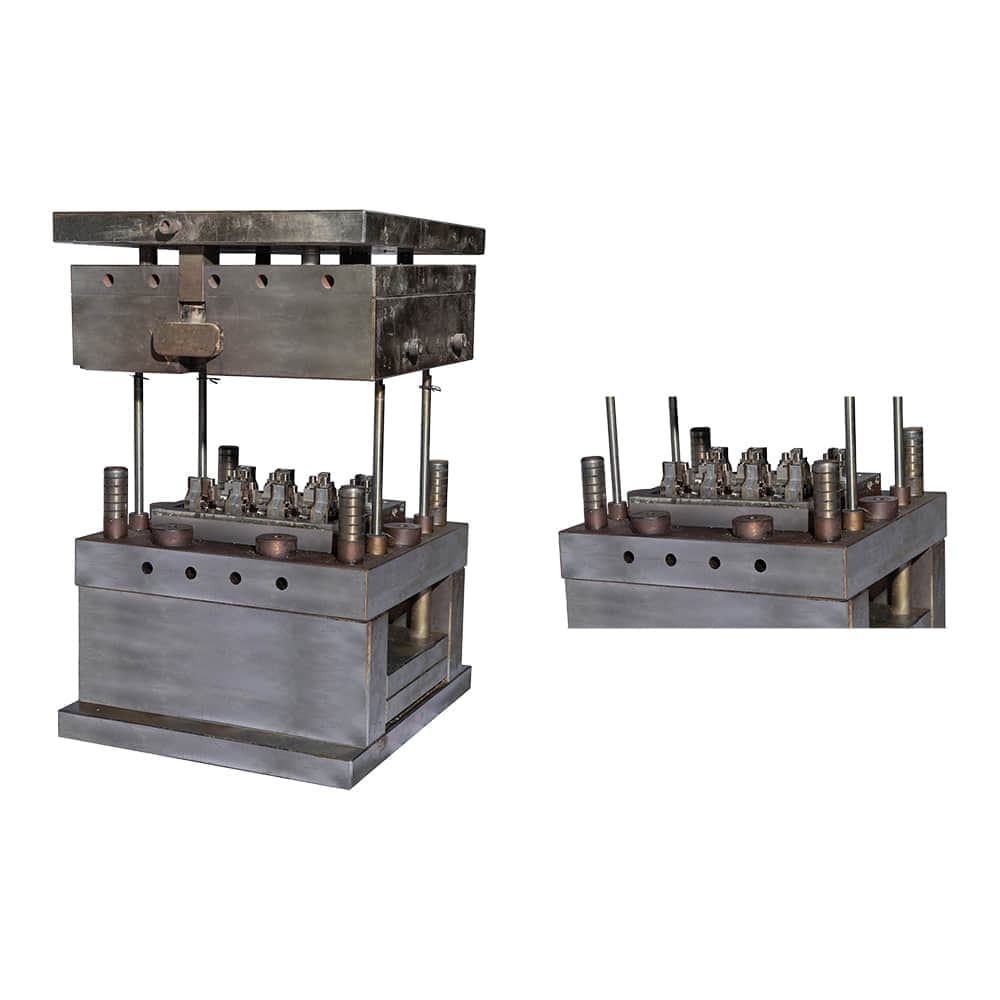

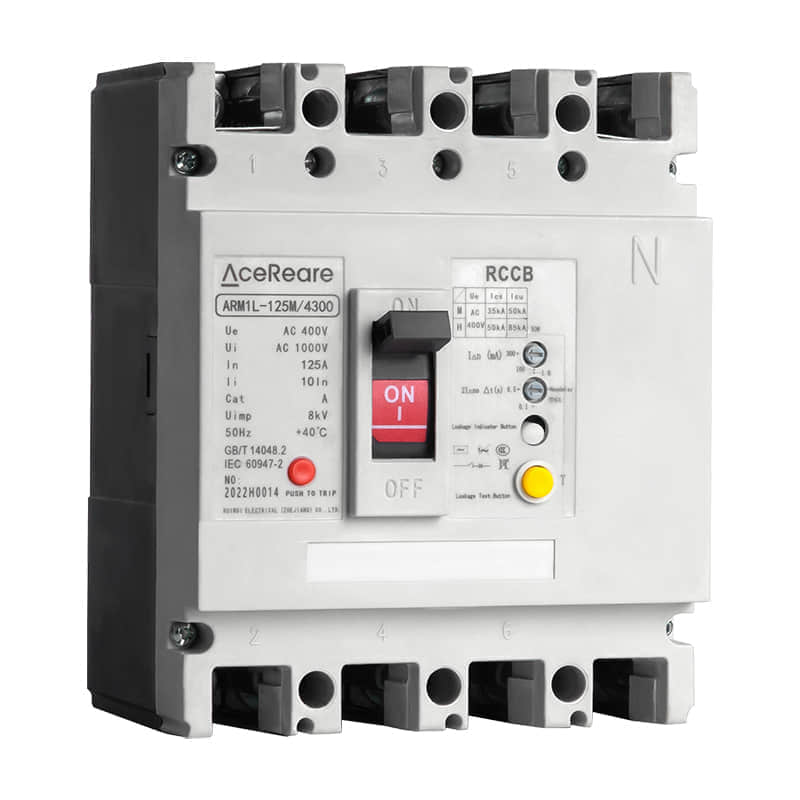
One of the most significant advantages of SMC molding is its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision. Manufacturers can create intricate designs and geometries that would be challenging or cost-prohibitive to achieve through other manufacturing methods. This makes SMC molding particularly attractive in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, where design innovation and lightweight yet robust components are paramount. Furthermore, SMC molding offers exceptional mechanical properties to the finished products. The incorporation of glass fibers provides enhanced strength and stiffness, making SMC-molded parts capable of withstanding heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions. This makes them an excellent choice for exterior automotive panels, structural components, and enclosures for industrial equipment. Apart from mechanical advantages, SMC molding also contributes to improved production efficiency. The process allows for high-volume production with relatively short cycle times. The ability to mold multiple parts simultaneously in a single cycle further optimizes manufacturing time and reduces overall production costs. Additionally, the low material waste associated with SMC molding aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices, appealing to environmentally conscious industries and consumers. SMC molding’s versatility extends to its surface finish options. Manufacturers can achieve a smooth and paint-ready surface directly from the mold, reducing the need for extensive post-processing. Alternatively, various textures and patterns can be incorporated into the mold to create unique surface aesthetics, eliminating the need for additional decorative layers. In recent years, advancements in material science and technology have further expanded the horizons of SMC molding. New resin formulations offer improved heat resistance, flame retardancy, and chemical durability, widening the range of applications in industries requiring compliance with stringent regulations. Additionally, innovations in mold design and simulation tools enable manufacturers to optimize the molding process, predicting potential challenges and ensuring high-quality output. However, like any manufacturing process, SMC molding is not without its challenges. Proper handling and preparation of the SMC material are crucial to achieving consistent results. Moreover, the initial investment in mold design and tooling can be substantial, which may pose a barrier for smaller manufacturers or those considering short production runs. In conclusion, SMC molding stands as a testament to the ongoing evolution of manufacturing techniques. Its ability to produce intricate, durable, and cost-effective parts has cemented its role in various industries. As technology continues to advance, SMC molding is likely to witness further refinements, making it an even more attractive option for innovative and sustainable production. Whether in automotive engineering, aerospace technologies, or consumer goods manufacturing, SMC molding is set to shape the future of how we create and assemble.